Technology in healthcare has never been more powerful, or more overwhelming. Every new tool promises to save time, improve accuracy, and reduce burnout, yet many end up creating more complexity than clarity.
Yes, AI can be a powerful tool to help reduce the time that doctors and administrators spend on documentation. But the real challenge when building a tool like AI doctor notes is building it in a way that feels intuitive, effortless, and usable for every physician, especially those who aren’t tech-savvy.
At Aloa, we build tools that fit how care teams already work: secure, compliant, and downright usable. Our approach centers on creating AI that feels natural in a clinician’s hands and genuinely makes their day easier.
And in this guide, you'll get:
- A clear playbook for designing physician-friendly AI tools
- The nuts and bolts of speech-to-note technology that doctors trust
- Real rollout strategies that get adoption across care teams
- Lessons from Aloa’s own healthcare AI builds that prove smart tech can feel simple
Because when AI feels natural, doctors get time back and patients get better care.
TL;DR
- Doctors spend 16 minutes per patient on notes; over 60% cite documentation as a top cause of burnout.
- Most AI tools fail because they’re built for technologists, not clinicians.
- The best AI doctor notes are invisible: one tap to start, no setup, no distraction.
- Core design rules: instant activation, background processing, intuitive use, device flexibility, and verified accuracy.
- Technical backbone: clinical-grade speech recognition, NLP note generation, and continuous learning for 99%+ accuracy.
- Results: up to 75% less documentation time; about 2–3 hours saved daily.
- Aloa builds HIPAA-compliant, physician-tested AI tools that fit clinical life seamlessly.
Why Non-Tech-Savvy Doctors Need Different AI Design Principles
AI doctor notes use artificial intelligence to listen during a patient visit and automatically turn that conversation into structured clinical notes. This automation reduces time spent typing or dictating, helping clinicians focus more on patients instead of paperwork.
Doctors work in a fast, high-pressure rhythm: listening, diagnosing, deciding, and moving quickly from one patient to the next. Their focus shifts constantly, and every second counts. That’s why AI tools built for healthcare need to feel invisible, fitting naturally into how doctors already work.
It’s also why the usual AI design playbook falls flat. Most AI products are built for users who have time to experiment, explore, and tinker. Doctors, however, need software that behaves predictably, instantly, and quietly, tools that disappear into the workflow.
Picture this. A physician launches a documentation tool that demands:
- Logging into a separate dashboard
- Granting microphone permissions again
- Choosing a note type from a dropdown list
- Waiting through another progress bar
It also doesn’t perform as anticipated every time, which led to three people knocking on the office door before lunch on the very first day. The odds that tool survives a week? Pretty slim.
Particularly in healthcare, complexity kills adoption. When technology feels like another hurdle, people find shortcuts (or drop it altogether).
That’s why “non-tech-savvy” should be the target user base for AI tools to succeed in healthcare. Not because doctors don’t get AI, but because the environment requires it of the tool.
Consumer AI vs. Clinical AI
Consumer AI, think chatbots or voice assistants, is designed for lower-stakes situations. If your virtual assistant mishears “basil” as “bagel,” no harm done. In healthcare, a wrong transcription could change a diagnosis. Clinical AI operates in a world where accuracy, traceability, and compliance are everything. Though even with AI support, care from an online psychiatrist remains essential for mental health treatment.
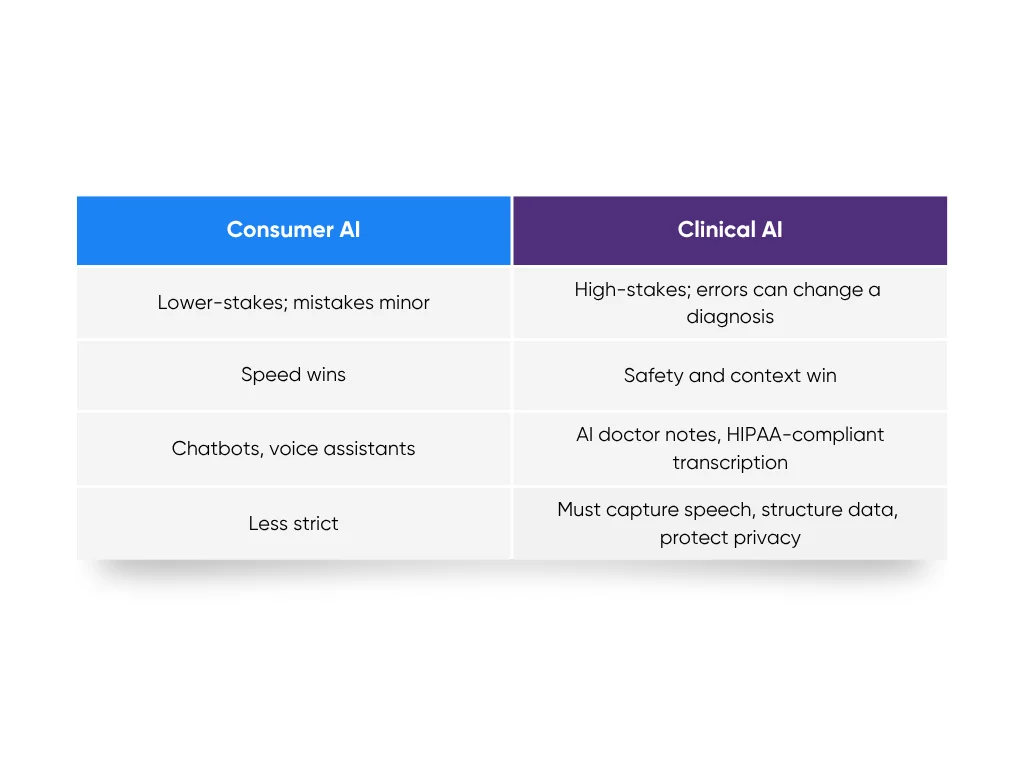
In consumer tech, speed wins. In healthcare AI, safety and context win. That’s why AI doctor notes need a different rulebook. They have to capture speech, structure data, and protect privacy all at once. When we built our HIPAA-compliant medical transcription tool at Aloa, that balance (speed without shortcuts, automation without losing control) was the foundation.
What Doesn't Work
Here are the most common ways “AI-for-doctors” tools fall apart:
- Multiple logins that break visit flow
- Setup processes that need training or IT support
- Unclear value, where the time savings never show up
- Inconsistent accuracy, missing vital medical terms
Each friction point drains trust. Even good technology fails when it doesn’t match the rhythm of a clinic.
Designing for Real Life in Medicine
Physician-friendly AI isn’t about slick dashboards or extra settings. It’s about invisibility. The best tools start in seconds, capture conversation naturally, and hand back structured notes without fanfare. When done right, doctors barely notice the tech. Only that their evenings end earlier.
We saw this firsthand while building our AI medical transcription platform at Aloa. By removing setup hurdles, automating formatting, and baking HIPAA safeguards into every layer, we built a tool clinicians trusted from day one. That same design mindset fuels our work on AI doctor notes: simple, secure, and built around how doctors actually work.
When technology finally fits the pace of care, doctors stop feeling “non-tech-savvy.” They start feeling supported. And that’s when AI starts doing what it promised all along.
The 5 Core Design Principles for Building AI Tools for Non-Tech-Savvy Doctors
Designing AI doctor notes that real clinicians will use takes more than technical skill. It takes empathy. The best healthcare AI doesn’t demand attention or training. It blends into the rhythm of care, speeds up the tedious parts, and earns trust through reliability. These five design principles make that happen:
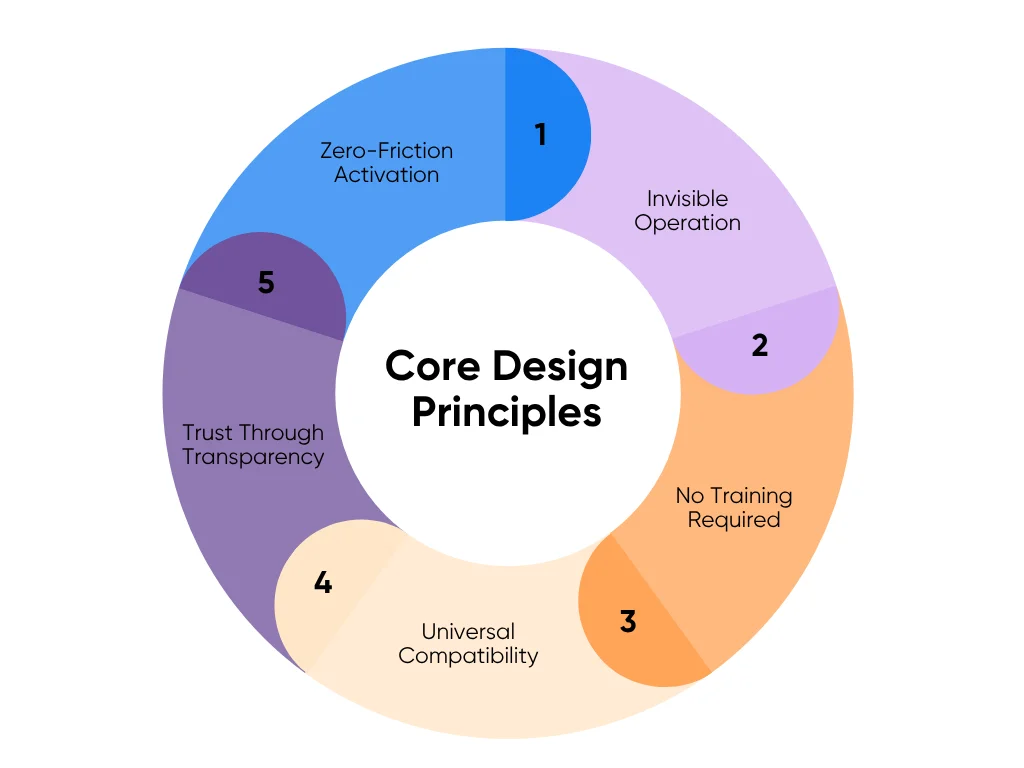
1. Zero-Friction Activation: One Button to Start
Zero-friction activation means the AI is ready before the user even thinks about it. No setup screens. No hidden menus. No “getting started” wizard. One tap, and it’s recording.
In clinical life, every second counts. If a doctor has to reselect microphones, grant permissions, or log in again between patients, the tool becomes another burden. When a physician enters the exam room, they want to start documenting, not troubleshooting.
Smart systems solve this with auto-detection and session memory. They remember user preferences, calibrate audio automatically, and launch instantly. Leading healthcare tools make the process feel like pressing “record” on a phone: simple, fast, predictable.
2. Invisible Operation: AI That Works in the Background
Ambient AI is designed to be unseen. It listens, learns, and documents without ever demanding attention. The clinician shouldn’t have to “manage” it. It quietly handles transcription, voice separation, and data structuring in real time.
Behind the scenes, it relies on real-time speech recognition, speaker identification, and medical language models tuned for accuracy and context. Updates appear within seconds, not minutes.
This design restores something rare in healthcare: undivided attention. When the tech stops asking for focus, the patient gets it instead.
3. No Training Required: Intuitive from First Use
Every clinician knows the trap of “time-saving software” that requires hours of tutorials. That’s an immediate no. True physician-friendly AI passes the five-minute test: If you can’t use it confidently in five minutes, it failed.
The best AI interfaces reuse what’s already familiar. Record, stop, save; nothing new to learn. Buttons look like the ones on a phone recorder. Icons feel intuitive. Advanced settings appear only when needed through progressive disclosure to keep things simple while still allowing power users to explore more.
Training time in healthcare is expensive. Every minute spent learning software is a minute away from patients. But self-explanatory design isn’t minimalism; it’s respect for limited attention.

That’s the standard we follow when designing tools at Aloa: open the app, start working. No walkthroughs, no onboarding decks. It just makes sense.
4. Universal Compatibility: Works on Any Device
Healthcare doesn’t stop at a desk. A doctor might review labs on a desktop between patients, add quick notes on a tablet during rounds, and check updates from their phone after hours. Their tools should move seamlessly with them, wherever they’re working.
Universal compatibility means the AI doctor notes system runs seamlessly across all devices (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, or browser) without special hardware or complicated installs. It also connects lightly with electronic health record (EHR) systems, syncing structured data securely without overloading them.
The key is light integration. Instead of replacing the EHR, the AI complements it. It passes notes into patient charts through APIs. No new tabs, no copy-paste loops.
Flexibility also means equal performance across in-person visits and telehealth. Whether documenting in a clinic or during a video consult, the experience stays smooth and consistent.
That’s how good design should feel: a tool that follows you instead of forcing you to follow it.
5. Trust Through Transparency: Traceability and Verification
In healthcare, accuracy isn’t optional; it’s ethical. No doctor will trust data they can’t verify.
Traceability makes every AI-generated line auditable. Each statement links to its original audio source. One click lets the doctor hear exactly where that line came from. It’s also clear what text was generated by AI and what was added or edited by the clinician.

Transparency replaces uncertainty with confidence. It allows quick fact checks, easy corrections, and verified documentation, without slowing anyone down.
This level of clarity satisfies HIPAA compliance, internal audits, and quality control. It protects both clinicians and organizations by showing how data moved from conversation to chart, step by step.
When verification feels effortless, trust becomes automatic.
These five design principles turn technology from a time sink into a time saver. That’s how clinical documentation AI stops being a “nice-to-have” and becomes a dependable teammate. When AI fades into the background, doctors stay present, patients feel heard, and care feels human again.
Building the Technical Foundation: How AI Medical Transcription Actually Works
Design principles make an AI doctor notes tool usable. The technical foundation makes it trustworthy. For AI to work invisibly in a clinic, it needs a finely tuned blend of audio capture, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning that constantly improves accuracy. This is the behind-the-scenes engineering that turns a live conversation into a clean, structured clinical note.
Audio Capture and Clinical Speech Recognition
Audio capture is where everything starts. It’s how the AI listens, interprets, and begins turning the real-world noise of a clinic into usable text.
The difference between general speech-to-text and clinical speech recognition is huge. A consumer tool can handle a podcast or grocery list, but a doctor-patient exchange moves fast and is packed with medical shorthand, abbreviations, and complex terms. A general model might hear “metoprolol” and write “metro pole.”
Clinical-grade AI is built differently. It’s trained on thousands of hours of medical recordings, learning the rhythm, tone, and interruptions that define real patient encounters. It recognizes shorthand, self-corrections, and interjections (“Hold on, any allergies?”) that confuse normal transcription tools.
Speaker identification adds another critical layer. The system labels who’s talking (doctor or patient) based on tone and cadence. That labeling makes it possible to structure the note correctly later.
Under the hood, the engine relies on:
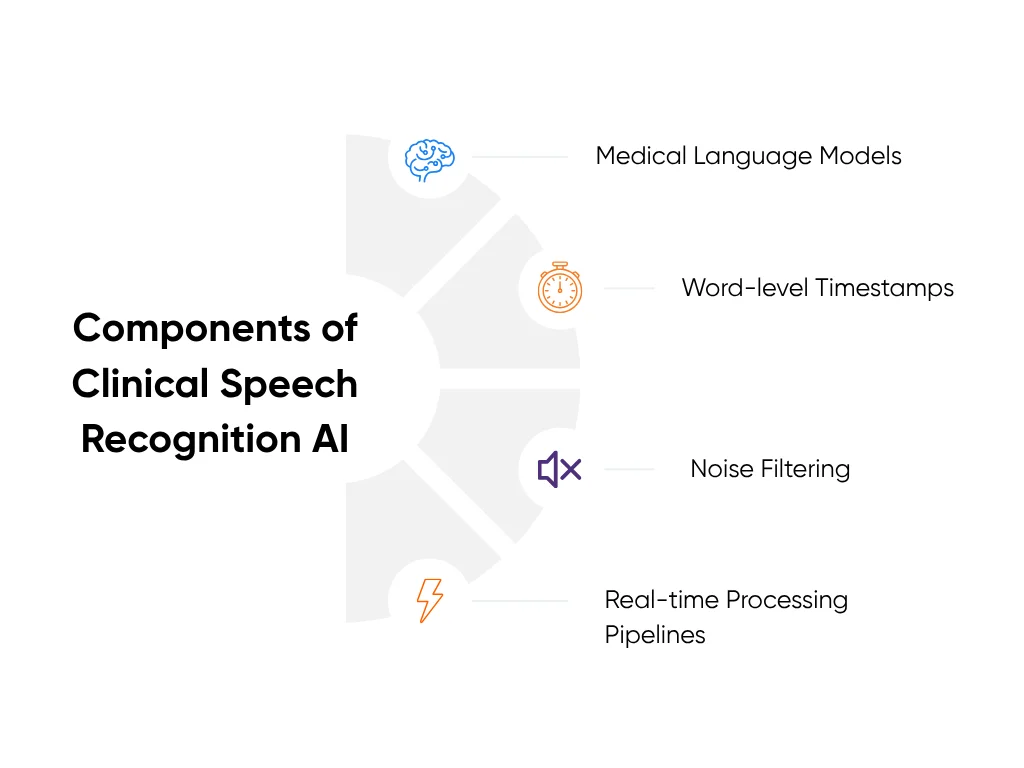
- Medical language models fine-tuned for healthcare vocabulary
- Word-level timestamps that keep transcription aligned with audio
- Noise filtering to cut out background sounds like monitors and hallway chatter
- Real-time processing pipelines that transcribe as the conversation unfolds
Advanced systems like AWS HealthScribe use domain-specific models built for this environment. They detect clinical intent, handle complex dialogue, and maintain context even when speech overlaps. The result is text that captures not just words, but clinical meaning, ready for deeper processing.
This is the first place where AI scribes earn trust: by keeping up with real-world clinical speed and accuracy without missing a beat.
Natural Language Processing and Note Generation
Once the system has a transcript, NLP takes over. It’s how the AI understands what was said, extracting meaning, identifying medical facts, and organizing everything into a structured note.
The AI detects key details: symptoms, medications, lab values, diagnoses, and treatment plans. It can tell the difference between “patient denies fever” and “patient reports fever.” It knows “metformin twice daily” is a prescription, not small talk.
To make the note usable, NLP organizes that information into familiar clinical structures like SOAP notes (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and Plan):

- Subjective: Patient-reported symptoms and history
- Objective: Observed data such as vitals and test results
- Assessment: The clinician’s impressions or working diagnosis
- Plan: The treatment steps, orders, and follow-ups
Behind the scenes, algorithms perform dialogue classification to filter out small talk and isolate what matters clinically. They also use template matching to adapt notes for different visit types, from urgent care to primary care follow-ups.
More advanced systems automatically output EHR-ready notes, placing the right information in the right chart fields for review and sign-off. No copy-paste. No reformatting.
At Aloa, this structured NLP workflow is core to our HIPAA-compliant medical transcription builds. We designed our systems to convert spoken language into organized, editable notes that slide naturally into existing workflows. Doctors described it as “what we already do; just faster, cleaner, and less draining.”
Accuracy and Continuous Learning Systems
In clinical AI, accuracy isn’t optional. A single transcription error can alter meaning, so top systems aim for 99% or higher accuracy. That level of precision comes from continuous learning.
A continuous learning system means the AI evolves with use. It learns from the doctor’s edits and adjusts accordingly. Every correction becomes feedback that fine-tunes its models, gradually shaping the system to match the user’s vocabulary, accent, and style.
Behind the scenes, several mechanisms make this work:
- Feedback Loops: Every edit informs the next prediction.
- Adaptive Models: The AI personalizes over time for each clinician or specialty.
- Accuracy Monitoring: Dashboards track metrics like word error rate and correction frequency.
- Quality Assurance Cycles: Ongoing validation ensures long-term reliability and compliance.
Over time, the tool starts to “speak” the clinician’s language. It picks up preferred phrasing, whether they write “BP normal” or “blood pressure within range,” and molds to their rhythm.
This personalization turns technology into partnership. The AI no longer feels foreign; it feels like a teammate.
In healthcare, that trust takes time to build, but continuous learning accelerates it. The more the tool is used, the sharper it becomes, without ever needing to stop or retrain from scratch.
Together, these layers (clinical speech recognition, NLP note generation, and continuous learning) form the technical backbone of every successful AI doctor notes system. They make the tool feel effortless on the surface because the complexity is buried beneath it.
That’s the balance Aloa builds for: empathy on the front end, precision on the back end. The clinician never sees the algorithms or tuning cycle. They just see more time for their patients, fewer after-hours charting sessions, and notes that finally feel like they wrote themselves.
The Complete User Experience: From Patient Conversation to Clinical Note
The beauty of a well-designed AI doctor notes system is that it feels effortless. What happens under the hood (real-time transcription, medical term recognition, natural language processing) is invisible. From the doctor’s point of view, the process feels simple, almost like the tool isn’t there at all.
Here’s what that experience looks like step by step:
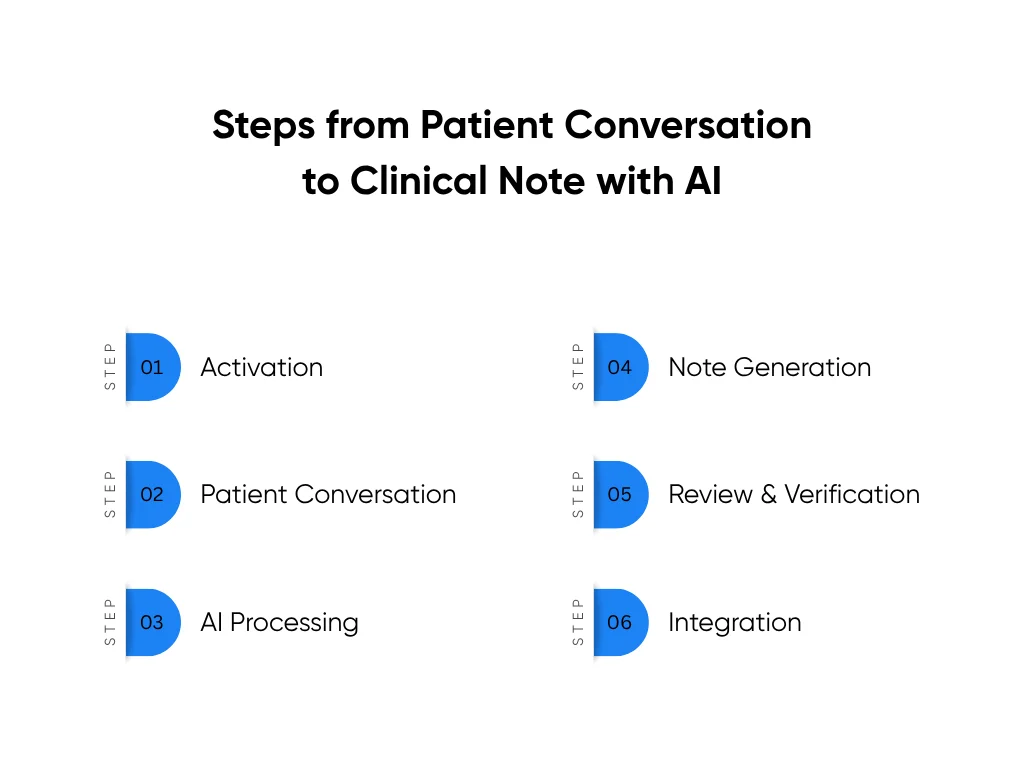
Step 1: Activation (5 Seconds)
The doctor opens the app or clicks the integration button inside their existing workflow. That’s it. No setup, no logins, no waiting screens.
One tap starts the session. A small visual indicator confirms recording, but it stays out of the way. The AI is live and listening, and the clinician can get right to the conversation.
Traditional documentation starts with a delay: loading EHRs, finding templates, adjusting windows. AI activation takes seconds instead of minutes, setting the tone for the rest of the workflow.
Step 2: Patient Conversation (10–20 Minutes)
Once activated, the AI fades into the background. This is where ambient AI earns its name. It listens quietly while the doctor focuses fully on the patient.
There’s no typing, no toggling screens, and no mental multitasking. The doctor can make eye contact, pick up emotional cues, and stay present in the conversation. The patient gets their full attention, not half of it lost to a keyboard.
During this phase, the system automatically distinguishes between voices, filters out background noise, and processes speech in real time. The doctor doesn’t need to prompt or correct it. The workflow feels completely natural.
Compare that to traditional documentation, where every two sentences of dialogue lead to ten clicks and two minutes of typing. AI flips that equation. Doctors get back nearly 90% of the time they’d normally spend documenting while seeing the same number of patients.
A 2024 JAMA Network Open study found that physicians using ambient AI scribes reported significant reductions in workload and improved patient interaction. These firsthand experiences mirror what most healthcare teams feel once documentation becomes invisible.
Step 3: AI Processing (Real-Time)
As the visit unfolds, speech recognition converts audio to text, labeling the doctor and patient automatically. NLP models extract clinically relevant data (symptoms, medications, vitals, and plans) and begin organizing them into structured note sections in the background.
All of this happens invisibly. There’s no progress bar or delay. The AI listens, interprets, and builds the framework for a complete note as the conversation happens.
Traditional speech-to-text tools stop at transcription. A doctor would still have to clean up, structure, and edit those notes later. With AI doctor notes, that’s already done before the visit ends.
Step 4: Note Generation (Seconds After Visit Ends)
As soon as the session stops recording, the full clinical note appears, organized, formatted, and ready to review.
Every medical term is spelled correctly. Medication names, dosages, and instructions are placed in the right sections. The note automatically follows the clinic’s preferred format: SOAP, free-text summary, or custom EHR layout.
What used to take 15–20 minutes of typing and reformatting now takes seconds. The doctor doesn’t have to remember what was said; the AI already captured it.
This is where the real time savings become obvious. Across 20 patient visits a day, that’s roughly four hours of documentation reduced to under one.
Step 5: Review and Verification (2–3 Minutes)
Next comes a quick review, usually just a few minutes. The doctor scans the note, clicks any sentence to reveal the original transcript, and makes small edits if needed.
Each edit teaches the AI. The system records corrections and uses them to improve future accuracy for that specific clinician. Over time, it starts writing in their voice, using their preferred phrasing and formatting style.
In traditional documentation, reviewing a note means proofreading from scratch. Here, it’s about confirming accuracy and moving on. The mental load drops dramatically, and the doctor’s evening hours stop disappearing into “charting time.”
Step 6: Integration (One Click)
Once approved, the note transfers directly to the EHR with a single button. The system auto-populates the correct fields, whether it’s the assessment, plan, or medication list.
There’s no exporting, no manual entry, and no switching between apps. The doctor presses one button, the EHR updates, and the visit is complete.
By the time the next patient walks in, the documentation for the previous one is done.
The Time Equation That Changes Everything
The entire process, from activation to integration, takes three to five minutes instead of the 15–20 minutes typical of manual documentation.
That’s up to 75% less time spent on paperwork every day. For a physician seeing 20 patients, that means gaining back roughly four hours daily. Time that used to go into after-hours charting now goes into patient care, research, or simply rest.
The American Medical Association reported that one hospital network using AI scribes saved over 15,700 clinician hours in a single year, the equivalent of nearly 1,800 workdays returned to care delivery. That’s what happens when documentation stops being a task and becomes a background process.

When the user experience works like this, AI doctor notes don’t feel like technology. They feel like relief.
Critical Features That Make or Break Physician Adoption
Even the smartest system will fail if doctors don’t use it. The truth is, adoption in healthcare doesn’t come down to how advanced the model is. It comes down to how it feels to use. When the features fit clinical reality, trust builds naturally. When they don’t, they gather dust.
Here are the make-or-break features that separate tools doctors love from those they leave behind:
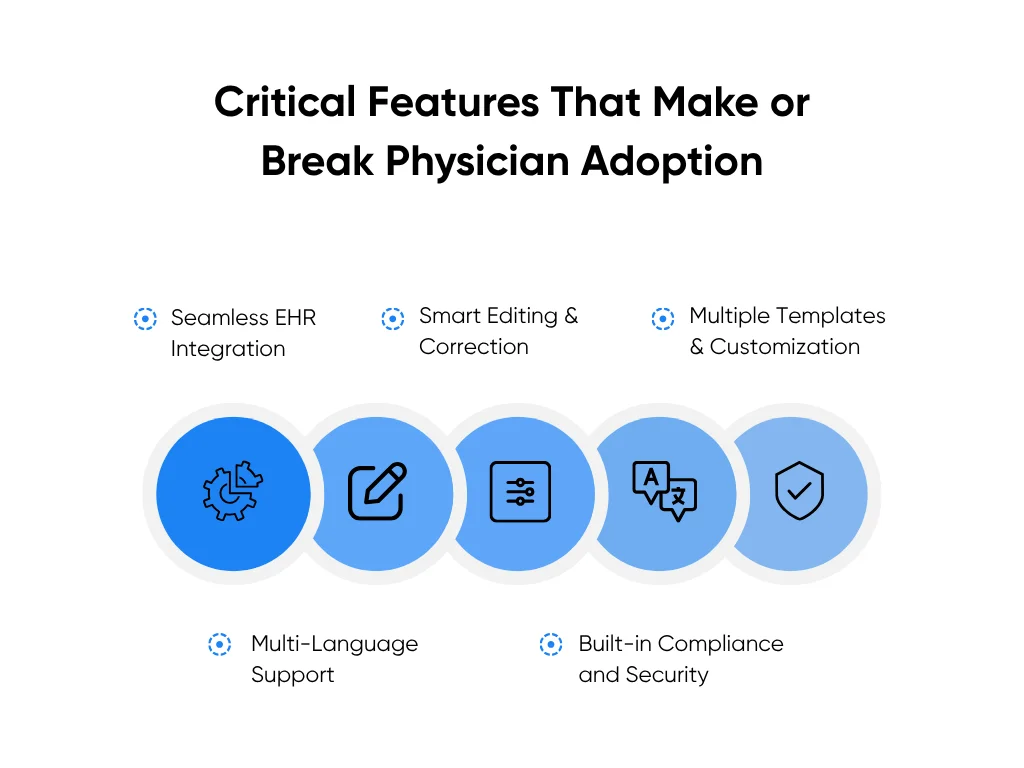
Must-Have Feature 1: Seamless EHR Integration
EHR systems are the backbone of modern care, and the number one friction point for most clinicians. Any AI tool that requires re-entering data, exporting files, or a complex setup immediately loses credibility.
Seamless integration means the AI fits into what already exists. It doesn’t demand a new workflow. It slips inside the current one.
That’s why the best systems use light integration footprints, connecting through secure APIs or FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) standards. This allows data to move safely between the AI and the EHR without needing deep IT intervention.
For the doctor, integration feels invisible. After reviewing a note, one click sends it straight into the correct EHR fields (assessment, plan, medications, vitals) automatically mapped and formatted.
This one-click handoff is critical. It saves minutes per encounter, prevents copy-paste errors, and keeps compliance intact. Leading solutions use this low-friction approach to make adoption seamless across systems like Epic, Cerner, and athenahealth.
When the AI feels like a natural extension of the EHR rather than another tab, it becomes a trusted assistant, not another burden.
Must-Have Feature 2: Smart Editing and Correction
Doctors think and speak fast. They need a tool that can keep up. Smart editing means the AI understands plain speech and adjusts on command.
Instead of typing corrections, the clinician can say:
- “Make this note more concise.”
- “Add that blood pressure under vitals.”
- “Remove patient-reported symptom about caffeine.”
These are natural language commands: plain, spoken phrases the AI interprets as actions. Combined with click-to-edit and undo options, the tool feels human-responsive, not rigid.
Every correction also becomes a teaching moment. The AI learns from physician input, gradually matching tone, phrasing, and documentation style. Over time, it starts producing notes that sound like the doctor wrote them.
A robust version history keeps every edit traceable, which supports clinical accountability. If a compliance officer or peer reviewer checks a record, they can see exactly how the note evolved.
This combination of flexibility and traceability transforms editing from tedious rework into quick collaboration.
Must-Have Feature 3: Multiple Templates and Customization
Medicine isn’t one-size-fits-all, and neither are notes. An urgent care visit looks nothing like a mental health consultation. A pediatric progress note differs from a cardiology follow-up.
That’s why customizable templates are non-negotiable. A strong AI doctor notes tool includes:

- Pre-built templates for common encounter types (physical exams, telehealth visits, chronic care follow-ups).
- Specialty-specific formats tailored to fields like dermatology, psychiatry, or orthopedics.
- Custom template creation without coding; simple drag-and-drop configuration.
The AI should also learn from how each doctor edits and structures notes. If a clinician consistently adds a section for “patient education,” the system should start generating it automatically.
This adaptability makes the AI feel personal. It fits into the clinician’s documentation rhythm instead of forcing them to adapt to it.
The Peterson Health Network, for example, implemented an AI documentation system that adapted templates dynamically to match each department’s workflow. Primary care physicians received structured SOAP notes by default, while behavioral health specialists got narrative templates emphasizing patient-reported insights. That flexibility reduced average documentation time by over 60% and eliminated the need for additional training.
When customization works this seamlessly, clinicians don’t have to change how they document. The technology changes for them.
Must-Have Feature 4: Multi-Language Support
Healthcare doesn’t speak one language. Many clinics serve patients who switch between English and another language mid-visit. The AI must keep up.
With multi-language support, the tool can recognize, transcribe, and translate across languages while preserving medical accuracy. For example, a patient might describe symptoms in Spanish while the doctor documents in English. The AI bridges that gap seamlessly.
A good system supports at least 25+ major languages, including Spanish, Mandarin, Hindi, and Arabic. It also incorporates cultural sensitivity in transcription, understanding idioms or phrasing unique to certain regions so translations stay true to intent.
Beyond transcription, note generation should happen in the physician’s preferred language, even if the conversation was multilingual. That ensures both compliance and clarity.
AI language models trained for healthcare use multilingual embeddings that keep clinical context intact across translations. When done right, the note is as accurate as if the entire exchange had been in one language.
This isn’t just inclusion; it’s accuracy. Real care happens in whatever language the patient feels safe in. The AI should too.
Must-Have Feature 5: Built-in Compliance and Security
No feature earns trust faster (or loses it faster) than compliance. In healthcare, the AI tool itself must shoulder the legal and ethical load, not the doctor.
That means every system must start with HIPAA compliance by default, backed by SOC 2 and HITECH certifications to verify security practices. These frameworks confirm that patient data stays encrypted in transit and at rest, access is strictly controlled, and every action is logged in an audit trail.
A strong AI doctor notes system should also come with pre-signed Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) so physicians don’t need to negotiate data use terms.
Other must-haves include:
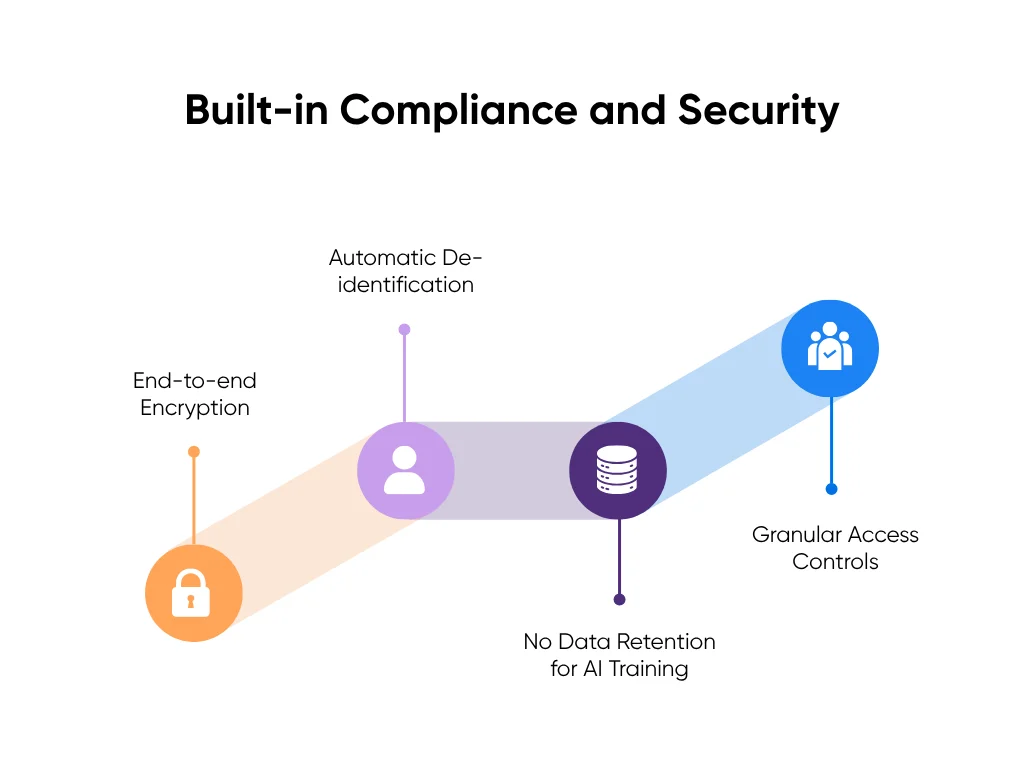
- End-to-end encryption for every audio and text file.
- Automatic de-identification that strips patient identifiers before AI model processing.
- No data retention for AI training, ensuring patient conversations never become training material.
- Granular access controls, so only authorized personnel can view or edit records.
When security is invisible yet absolute, adoption follows. Doctors won’t use tools they don’t trust with their patients’ information.
In Aloa’s healthcare AI projects, compliance isn’t a checklist. It’s part of the build. Every transcription system and AI workflow is architected with encryption, audit logging, and de-identification at its core.
That’s what turns a promising prototype into a product real physicians depend on.
Partner with Aloa to Build Physician-Friendly AI Tools
Building AI that doctors actually use takes more than great engineering. It takes understanding how care really happens. At Aloa, we design and build healthcare AI systems that blend technical precision with clinical practicality.
Our team works directly with physicians, clinic administrators, and innovation leads to create tools that fit naturally into everyday workflows. From HIPAA-compliant medical transcription to AI-powered documentation and clinical automation, every project begins with one simple question: Will this make a clinician’s day easier?
We bring deep expertise in AI and machine learning, natural language processing, and secure healthcare integrations, paired with hands-on experience in regulatory frameworks like HIPAA and HITECH. That combination helps us deliver systems that are compliant, reliable, and effortless to use.
Aloa provides end-to-end support, from discovery and design to deployment and optimization. We often start with early consultation sessions to explore your use case before a single line of code is written.
If your team is exploring AI doctor notes, medical transcription, or workflow automation, let’s design something that truly fits the way your clinicians work.
Key Takeaways
The best AI doctor notes systems don’t need applause. They just quietly get the job done. Great healthcare AI should disappear into the workflow.
When tech feels invisible, doctors gain hours back, patients get more focus, and care feels human again. That’s what we build at Aloa: AI that’s practical, secure, and simple enough to actually use.
Thinking about your next AI move? Let’s talk. You can also join our AI Builder Community or subscribe to our newsletter for real stories and lessons from the front lines of healthcare AI.
FAQs
Why do AI tools often fail with non-tech-savvy doctors?
AI tools often fail with non-tech-savvy doctors because they’re built for engineers, not everyday users. If a tool feels confusing or adds extra steps, it’s not practical for healthcare settings.
What’s the difference between general AI transcription and medical transcription?
General AI transcription just turns speech into text, like writing down what someone says in a meeting. Medical transcription not only writes it down but also understands medical terms, patient notes, and context so it doesn’t confuse “hypertension” with “attention.”
How long does it take to learn a well-designed AI transcription tool?
If it’s well-designed, it should take minutes, not days. A true physician-friendly tool passes the “five-minute test.” If a doctor can record, review, and approve a note on their first try, it’s built right.
How much time can doctors save with AI medical transcription?
On average, 2–3 hours per day. About 60–70% less time on notes. That’s 10–15 hours back each week. Enough to finish charts during clinic hours and still make it home for dinner.
How does Aloa build AI tools for non-tech-savvy physicians?
We start by learning how doctors actually work, then build tech that fits. One-click start, instant EHR sync, automatic compliance. Everything complex stays under the hood. We test with real clinicians until the tool feels invisible: AI that works quietly so doctors can focus on care.

