UX and product design play a crucial role in creating successful digital products. Good UX design improves user satisfaction, while effective product design ensures the product meets business goals. Together, they form a key part of design and development services, offering a seamless user experience that meets business objectives.
Aloa is a software agency specializing in top-notch design and development services. Our UX and product designers are experts in creating user-centered designs prioritizing usability and satisfaction. We provide transparent performance reports through our project dashboard and offer ongoing support to ensure your project stays on track and meets your expectations.
Based on our expertise and years of experience in providing design and development services, we’ve prepared this guide to explain what UX and product design are. We will tackle their differences and the benefits of aligning both aspects and share our top picks for companies that provide these services.
Let’s dive in!
UX Design vs. Product Design
UX and product design are essential in creating successful digital products through design and development services, but they have different focuses. UX design emphasizes user experience, while product design covers the product's overall creation, functionality, and aesthetics. Let's dig deeper into what each entails and their differences.
What Is UX Design?
UX Design, or User Experience Design, focuses on how users interact with a product or service. It aims to create a smooth, enjoyable, and meaningful experience for the user. This process involves researching user needs, behaviors, and pain points. UX web design experts create wireframes, prototypes, and user flows to ensure the product is easy to navigate.
What Is Product Design?
Product Design is creating a new product that solves a specific problem or meets a need. It involves planning, research, designing, and testing to ensure the product is functional and appealing. Product designers consider the user experience and the product's overall brand design look, feel, and functionality.
Key Differences Between UX Design and Product Design
Understanding the distinction between UX Design and Product Design is essential for anyone looking for design and development services. The key differences highlight how these two disciplines approach the design process and user experience.
1. Core Objectives
UX Design aims to create a positive user experience, ensuring the product is easy and enjoyable to use. In contrast, Product Design focuses on delivering a functional solution that meets market needs while considering the overall usability and aesthetics.
Example: Consider a mobile banking app. A UX designer's primary concern would be to make the app easy to navigate and use for customers. On the other hand, a product designer would also evaluate the app's compatibility with the bank's overall services and business model.
2. Scope of Work and Areas
The scope of work in UX Design focuses primarily on how users interact with a product. Conversely, Product Design encompasses the entire process of creating a product, including its functionality, appearance, and market viability.
Example: Think of a smartphone. A UX designer would focus on optimizing the user interface for easy navigation and efficient use of apps. On the other hand, a product designer would also consider the device's physical design, materials, and overall aesthetics.
3. User-Centricity and Customer Feedback
User engagement is crucial in UX Design, as it prioritizes understanding user needs and preferences through research and testing to gather valuable insights. In Product Design, client reviews and customer feedback help refine the product, ensuring it meets market demands and effectively solves real user problems.
Example: In optimizing the shopping experience for an e-commerce website, a UX designer prioritizes user research. Conversely, a product designer considers factors such as profitability, market competition, and scalability.
4. Timeline and Stages of Involvement
In UX Design, involvement typically occurs during the early stages of product development, focusing on research, wireframing, and user testing. Product Design spans the entire development cycle, from initial concept to final production, ensuring the product is functional and appealing.
Example: In the development process of a new mobile app, UX designers play a crucial role in defining the initial user experience. Subsequently, product designers assume the lead in crafting the visual elements and features of the app.
5. Skill Sets and Tools
UX Designers use tools like Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD for creating user personas and visualizing user experiences. Product Designers also use Figma and Sketch, along with Adobe Creative Suite, to design interfaces while considering business needs and market research.
Example: A website redesign involves various aspects. First, a UX designer primarily focuses on improving user navigation and functionality. Then, a product designer goes further by enhancing the visual elements and branding of the website.
Benefits of Aligning UX Product Design
Aligning UX and product design offers various advantages. When businesses integrate these two disciplines in their design and development services, they can unlock numerous benefits for their final product.
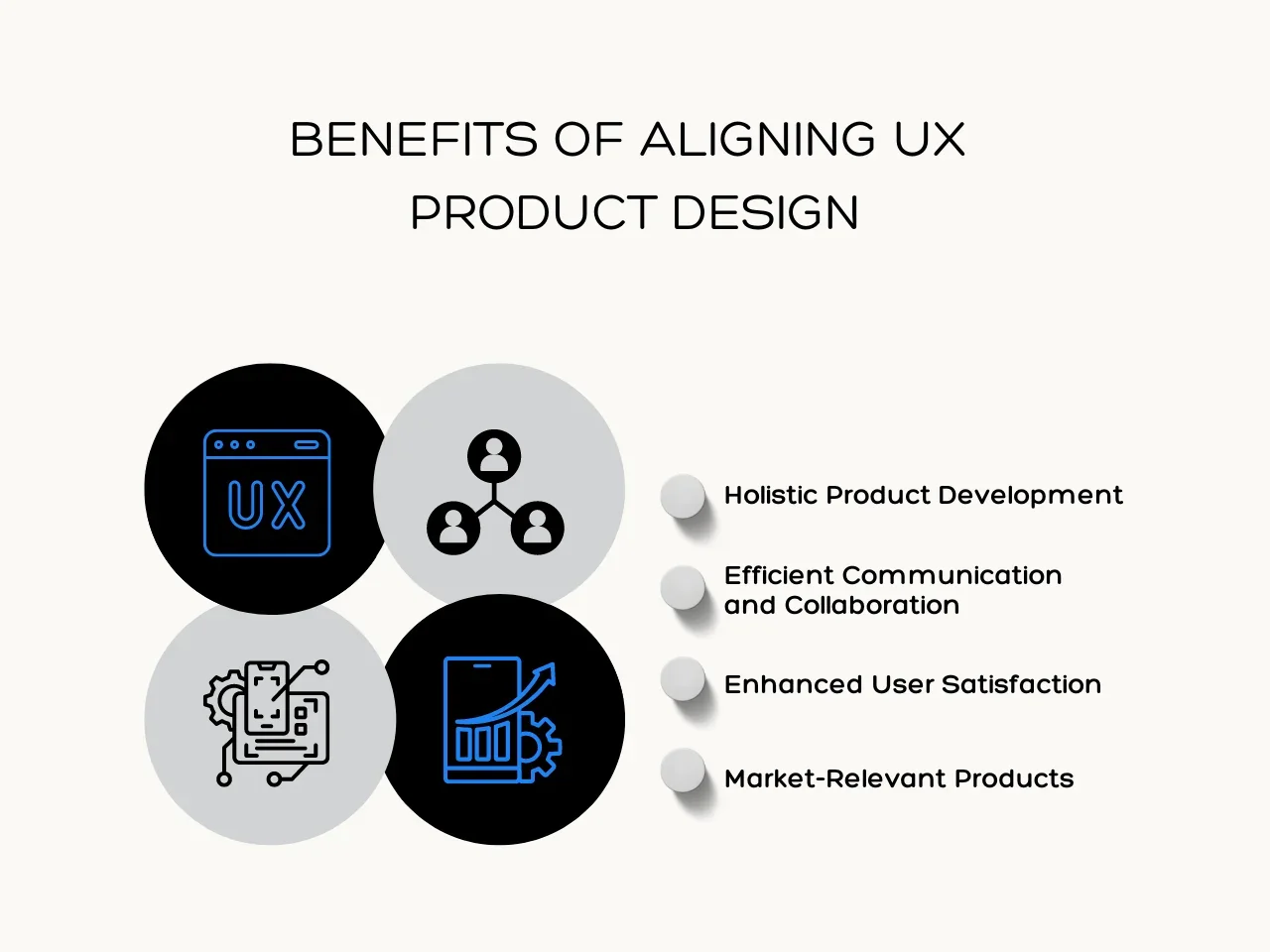
Holistic Product Development
Collaboration between UX and product design leads to a well-rounded approach to product development. UX designers focus on creating user-friendly experiences, while product designers manage the entire project from start to finish. This results in products that effectively meet the needs of their target audience through tailored design and development services.
Efficient Communication and Collaboration
Encouraging collaboration between UX and product design teams improves communication and problem-solving in project management. For example, in mobile app development, UX designers work closely with product designers, UI designers, and developers. This teamwork speeds up development cycles and improves project outcomes.
Enhanced User Satisfaction
The main goal of both UX and product design is to achieve user satisfaction, which ultimately drives business growth. When they work together, user feedback is regularly included in product development, ensuring quality work that helps create intuitive products that meet customer needs.
Market-Relevant Products
Involving product designers helps businesses understand market trends, competitor analysis, and new technologies while adhering to industry standards and best practices. For example, a product designer might find a market gap for a specific web app tool, which can be added to the product roadmap for a competitive advantage.
Efficient Resource Allocation
Balancing user needs with business goals is essential. While UX design aims to satisfy users, product design also considers cost-effectiveness and market viability. This collaboration helps avoid spending too much on features that don't meet business objectives or customer expectations. As a result, companies can allocate resources more effectively, focusing on what truly matters for both users and overall success.
6 Amazing Web Design and Development Services to Explore in 2024
As businesses embrace digital transformation, choosing the best website development company is essential for success. Let's explore the top 6 sites for web design and development services in 2024.
1. Aloa - Best for Web Design and Development Services On Time, On Budget, and in High Quality
Aloa is a global leader in helping businesses scale our web design and development services. Whether looking to staff multiple web design and development professionals or build a website, Aloa ensures you work with the best web designers and developers worldwide.
At Aloa, your software experiences will be on time, on budget, and in high quality. Our development process includes consistent updates on your project progress, regular check-ins, and consistent collaboration and communication. Our process ensures you receive top-quality design and development services while meeting industry requirements and standards.
Notable Features of Working with Aloa
- Extensive Partner Network: Aloa has vetted 10,000+ software agencies around the globe to identify and hire the best web designers and developers the industry has to offer.
- Rigorous Vetting Process: Every web designer and developer undergoes a thorough evaluation, ensuring they meet Aloa's stringent quality and proficiency standards.
- Transparent Performance Reports: Aloa ensures consistent updates on the project's progress and lets clients stay informed and confident with every step.
- Dedicated Support System: Aloa offers continuous support throughout the software journey, from initial consultations to project completion. We're here for you.
Aloa Pricing Plans
When hiring web design and development professionals, Aloa ensures clients link up with the ideal team within our partner network. Our Account Executives take the time to evaluate your needs and requirements. So, hiring on retainer? Let's chat about monthly discounts. Have a fixed scope of work? Let's get you a detailed estimation. Schedule a call or reach out to sales@aloa.co for a personalized consultation.
2. Digital Web Solutions (DWS) - Offers Comprehensive Digital Marketing Services
Digital Web Solutions (DWS) provides digital marketing services, including web design and development services. With a team of skilled professionals, DWS specializes in creating tailor-made solutions to elevate businesses' online presence. Their expertise extends across various industries.
The DWS team mainly prioritizes collaboration, working closely with clients to understand their objectives and deliver solutions that exceed expectations. With their dedication to staying updated with industry trends, clients can ensure they receive innovative and future-proof web designs.
Notable Features of Working with Digital Web Solutions
- Responsive Web Designs: Clients of digital web solutions can expect websites that generate leads and put their businesses at the forefront of visibility.
- Intuitive User-Interfaces: They provide thoughtful layout design, intuitive navigation menus, and interactive elements.
- Customized Client Experiences: Digital Web Solutions offers customized experiences that cater to individual needs and preferences.
Digital Web Solutions Pricing Plans
Digital Web Solutions offers clients tailored solutions in web design and development services. To get a breakdown of the cost, contact them via their website. You'll also have the chance to discuss project requirements based on your needs.
Whether you're a startup looking to establish a solid online presence or an established company aiming to revamp your website, DWS's comprehensive services cater to diverse needs.
3. UX Studio - Provides World-Class UI/UX Design and Optimization Services
UX Studio brings world-class expertise in creating visually appealing and user-friendly online storefronts. Their team of seasoned professionals understands the intricacies of ecommerce platforms. It is adept at crafting engaging user experiences tailored to boost sales and customer satisfaction.
UX Studio offers a comprehensive suite of services for ecommerce businesses, including custom website design, user research, and expert reviews. Their deep understanding of ecommerce dynamics enables them to provide tailored design and development services that drive conversions and enhance brand visibility.
Notable Features of Working with UX Studio
- Custom Ecommerce Designs: Tailored designs that resonate with your brand identity and captivate your target audience.
- Conversion Optimization: Strategies focused on maximizing conversions at every customer journey stage.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Ensuring smooth shopping experiences across all devices, enhancing accessibility and engagement.
UX Studio Pricing Plans
UX Studio offers flexible pricing plans tailored to the needs of ecommerce businesses, ranging from basic design packages to comprehensive optimization services. Fill out the contact form on their website to connect with UX Studio and take the next step towards achieving your goals and specific needs.
4. Suffescom Solutions - Specializes in Ecommerce Web Design
Suffescom Solutions specializes in providing comprehensive solutions for ecommerce web design services. With a focus on user experience and market-leading designs, they bring expertise in crafting a visually appealing and responsive design for online ecommerce stores that drive conversions.
Clients partnering with Suffescom Solutions for ecommerce web design and development services benefit from tailored solutions that elevate their online presence. From intuitive user interfaces to seamless navigation and secure payment gateways, Suffescom ensures that clients' ecommerce platforms stand out amidst competition.
Notable Features of Working with Suffescom Solutions
- Customized Ecommerce Designs: Tailored designs to reflect brand identity and enhance user experience.
- Integrated Payment Gateways: Secure and convenient payment processing for enhanced customer trust.
- Scalability: Ecommerce platforms designed to grow alongside businesses, accommodating increased traffic and transactions.
Suffescom Solutions Pricing Plans
Suffescom Solutions is a custom website development company that offers flexible pricing plans. You can complete the contact form on their website to connect with their business development team and address your digital requirements.
They cater to a diverse clientele, including ecommerce businesses seeking to establish or enhance their online presence.
5. Appnovation - Offers Custom Web Development for Enhanced User Experience

Appnovation is a UI design and software development agency offering innovative solutions to clients worldwide. With a focus on delivering seamless digital experiences, Appnovation empowers businesses to achieve their online goals effectively.
From e-commerce platforms to content management systems, they possess the technical expertise to create versatile and scalable websites. Additionally, their expertise in user experience (UX) design ensures that websites are visually appealing and intuitive to navigate.
Notable Features of Working with Appnovation
- Technology Expertise: With expertise across a wide range of technologies, like cloud computing, AI, blockchain, and more, Appnovation delivers innovative solutions.
- Seamless User Experience Design: Appnovation crafts engaging interfaces that optimize usability and conversion rates.
- Ongoing Support and Optimization: They provide ongoing support and optimization for web development services to help business owners maximize the value of their digital investments.
Appnovation Pricing Plans
Appnovation is a design and development service provider that provides tailored solutions based on client needs and web design objectives. Contact their team via their website to schedule a call so you can discuss price plans, project requirements, and expected outputs.
Startups and small business owners looking for web design and development services that prioritize innovation and creativity benefit from working with Appnovation experts.
6. WSI World - Provides Online Business Solutions and Lead Generation
WSI World is a development and web design company offering potential partners a comprehensive suite of global web design and development services. What sets WSI World apart is its holistic approach to digital solutions. Beyond merely designing and developing websites, they focus on driving measurable business outcomes for their clients.
As they integrate digital marketing strategies, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) techniques for organic traffic, and data analytics, WSI World ensures that every website they create looks impressive and delivers tangible traffic, conversions, and revenue growth results.
Notable Features of Working with WSI World
- Proven Track Record: Their team's track record of delivering cohesive digital strategies makes them an excellent choice for web design and custom software development services.
- Data-Driven Approach: Using a data-driven approach, WSI World enables businesses of all types to meet their online goals and objectives,
- Global Clientele: With a global clientele, their team is well-versed in working with businesses of all sizes, industries, and locations.
WSI Pricing Plans
Those looking to work with WSI World should contact their representatives via their website to find a consultant regarding their pricing tiers. Their team will walk you through designing and developing your website based on your goals and objectives.
Companies looking for integrated solutions that combine website redesign, custom website development, and digital marketing will find WSI World's offerings valuable.
Key Takeaway
Mastering UX and product design is crucial for creating successful digital products through effective design and development services. These disciplines work together to align user needs with business goals. Understanding their differences and benefits allows you to make informed decisions that improve your product development process.
Leveraging design and development services can boost user satisfaction and loyalty. As you explore the options available, remember the importance of collaboration between designers and developers. This teamwork will help you create intuitive and engaging products that stand out in the market.
Need help building a user-centric digital product? Aloa is the best web design company to help you overcome these challenges by providing expert design and development services. Our team of skilled UX and product designers collaborates closely with you to ensure your product is user-friendly and functional.

