Employment contracts serve as the foundation for a stable working relationship, defining the terms of employment, job duties, and employment rights crucial in the modern workplace. Choosing the right types of employment contracts is essential for business success, ensuring legal protection and clarity for employers and employees. Each contract type addresses specific business needs and employment relationships, from permanent employment contracts to temporary and casual employment contracts.
At Aloa, we understand the complexities of forming the right employment agreements. With our expertise in software outsourcing, we guide businesses and startups in navigating these critical choices. We ensure that every employment contract, whether permanent or temporary, aligns with the business's strategic goals and the specific tasks at hand. Our approach minimizes legal risks and enhances job training and employee contract satisfaction.
Leveraging our extensive experience, we've compiled this guide that dives into the various types of employment contracts, including sections on legal contracts templates. It details the main contract types for employment and explores the considerations when choosing the right one. Afterward, you will understand how to tailor employment agreements to match contract type, number of hours, and specific end dates to your hiring needs, ensuring compliance and flexibility.
Let's get started!
7+ Types of Employment Contracts to Consider When Hiring

When hiring, understanding the diverse landscape of employment contract types is crucial. Each contract type offers unique benefits and considerations tailored to meet business needs and legal requirements. Let's explore seven types of employment contracts and their respective use cases to help you streamline your hiring process.
1. Permanent (Full-Time) Contracts
Permanent contracts are types of employment contracts where employees agree to work full-time indefinitely. This arrangement ensures job security and typically includes various benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid vacations. Employers benefit from the continuity and deep expertise that full-time employees bring.
Use Cases of Permanent (Full-Time) Contracts
%2520Contracts.webp)
- Long-Term Projects: Companies often need stable, reliable teams for projects extending over several years. Permanent contracts provide the consistency necessary for complex, long-duration initiatives.
- Core Business Functions: For critical areas like management, finance, and product development, businesses prefer the reliability and invested interest that come with permanent staff.
- Development of Company Culture: Full-time employees tend to be more integrated into the company’s culture and ethos, promoting a stable work environment.
- Expertise in Niche Areas: Permanently hiring allows companies to retain individuals with specialized skills crucial for business operations, avoiding frequent retraining.
- Leadership Roles: Organizations typically fill leadership and executive positions with permanent contracts to ensure long-term strategic direction and vision.
When considering permanent employment contracts, businesses must weigh the benefits of employee stability and expertise against the need for flexibility in staffing. These types of employment contracts are best suited for roles requiring deep knowledge of the company and its processes, contributing significantly to the organizational foundation.
2. Fixed-Term Contracts
Fixed-term contracts are employment contracts where an employee works for a specific period set in advance. These contracts end on a predetermined date or upon completion of a project. They are highly beneficial for managing workforce flexibility and controlling costs, as they do not typically include the extensive benefits associated with permanent contracts.

Use Cases of Fixed-Term Contracts
- Seasonal Peaks: Retailers often hire additional staff on fixed-term contracts during holiday seasons to manage increased customer demand.
- Maternity or Sick Leave Cover: Organizations use fixed-term contracts to fill positions left vacant by employees on extended leave temporarily.
- Special Projects: Companies initiate projects with a clear endpoint, such as a product launch or market research, and employ staff on a fixed-term basis for the project duration.
- Testing New Markets: Companies might opt for fixed-term contracts to staff the trial phases without a long-term commitment when exploring new business areas or markets.
- Grant or Funding Specific Work: Institutions often hire staff on fixed-term work contracts specifically funded by grants or external funding, ensuring budget adherence and project focus.
When deploying fixed-term contracts, organizations should consider the precise nature of their needs and the project timelines. These contracts provide flexibility and cost management for temporary needs without the long-term financial commitments of permanent contracts, making them ideal for short-term projects and transitional workforce adjustments.
3. Part-Time Contracts
Part-time contracts are types of employment contracts where employees work fewer hours than full-time equivalents. These contracts offer flexibility and are often preferred by individuals who balance work with other commitments, such as education or caregiving. Employers benefit from managing payroll costs and the ability to staff hours according to business needs without the commitment of a full-time salary.

Use Cases of Part-Time Contracts
- Supplemental Workforce: Companies use part-time contracts to handle workload fluctuations without overstaffing.
- Skill-Specific Roles: Organizations hire part-time specialists for their expertise, which is needed only at certain times.
- Customer Service Positions: Retail and hospitality sectors often employ part-time workers to cover peak periods like evenings and weekends.
- Internships and Trainees: Students and trainees are frequently hired on part-time contracts to gain experience while pursuing their studies.
- Transitional Phases: Businesses in transition, such as startups and companies undergoing restructuring, benefit from the adaptability of part-time contracts.
When considering part-time employment contracts, balancing their flexibility with the need for consistent workforce availability is essential. These types of employment contracts are ideal for roles that do not require a full-time presence but are critical for specific operations or peak times.
4. Temporary Contracts

Temporary contracts are employment contracts used for hiring individuals for a specific, short-term period. This duration may be defined by a project’s needs or a specific term. One of the benefits of these contracts is to help meet project deadlines, cover unexpected staff shortages, or handle seasonal increases in workload.
Use Cases of Temporary Contracts
- Event Management: For large events, temporary staff are essential for logistics and customer service roles.
- Unexpected Absences: Companies often rely on temporary contracts to quickly fill gaps caused by sudden employee absences.
- Project-Specific Needs: Temporary contracts allow organizations to acquire specific skills for the duration of a project without long-term commitments.
- Peak Season Operations: Industries like tourism and agriculture use temporary contracts extensively during busy seasons.
- Regulatory Compliance Tasks: Temporary hires may be needed to manage short-term, intensive workloads like audit preparations or compliance checks.
Utilizing temporary employment contracts offers flexibility and workforce management options for businesses facing variable demands or specific short-term needs. Companies must manage these contracts effectively to benefit from the agility they provide without disrupting ongoing operations.
5. Freelance Contracts
Freelance contracts involve hiring individuals on a project or task basis without providing traditional employment benefits. Freelancers are typically self-employed and offer specialized services. This flexibility is advantageous for companies needing expertise irregularly and for workers desiring control over their workloads and schedules.

Use Cases of Freelance Contracts
- Creative Projects: Freelancers are often hired for their unique creative skills in marketing campaigns, graphic design, or content creation.
- IT and Web Development: Companies hire freelance IT professionals for website updates, system customizations, or to manage specific technology projects.
- Consulting Services: Freelancers provide consulting in finance, HR, and management, bringing external expertise to strategic projects.
- Research and Development: Freelancers can conduct specialized research or participate in development projects where their skills are needed temporarily.
- Operational Efficiency Projects: Skilled freelancers help optimize processes, such as workflow improvements or software implementation, without needing a permanent role.
Organizations must ensure clear communication of project scopes and deadlines when leveraging freelance contracts. These types of employment contracts benefit tasks requiring specialized knowledge or supplementing existing staff during peak workload periods.
6. Zero-Hour Contracts
Zero-hour contracts are types of employment contracts that do not guarantee a minimum number of work hours per week. Employees work only when needed, and their hours can vary widely from week to week. This flexibility benefits employers who experience unpredictable demand but can lead to instability for workers who may find it difficult to predict their earnings.

Use Cases of Zero-Hour Contracts
- Emergency Staffing: Companies utilize zero-hour contracts to have a pool of available workers during sudden increases in demand or unexpected staff shortages.
- On-Call Services: Industries such as healthcare and IT support often rely on zero-hour contract workers for on-call services during off-peak hours.
- Event Staffing: Zero-hour contracts are ideal for events that occur occasionally throughout the year, requiring staff on an as-needed basis.
- New Market Testing: Businesses entering new markets might use zero-hour contracts to quickly scale operations up or down based on immediate market response.
- Seasonal Industries: Zero-hour contracts in sectors like tourism or agriculture provide workforce flexibility that aligns with seasonal business fluctuations.
Zero-hour employment contracts offer unmatched flexibility for businesses. Consider, for example, a tour agency that hires a highly specialized tour guide for the beaches of Normandy only when their unique expertise is needed for specific tours based on demand, without guaranteeing fixed hours. However, these contracts require careful management to maintain a motivated and available workforce.Employers must balance operational needs with their employees' financial stability and satisfaction.
7. Consulting Contracts
Consulting contracts involve hiring experts to advise or manage specific business operations or strategies. These contracts are typically short-term and focused on particular goals. They allow companies to leverage external expertise efficiently without the overhead associated with full-time employment.

Use Cases of Consulting Contracts
- Strategic Development: Consultants often help companies craft strategies for expansion, reorganization, or entry into new markets.
- Technology Implementation: IT consultants are crucial for managing new software and systems deployment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Consultants with expertise in legal or regulatory matters guide businesses through compliance challenges.
- Operational Improvement: Consultants analyze existing operations and recommend efficiencies or improvements.
- Crisis Management: During times of crisis, consultants can provide the expertise needed to navigate complex situations effectively.
At its core, consulting contracts are essential for temporarily accessing specialized knowledge and skills. Companies considering these types of employment contracts should clearly define the scope and objectives of the consultancy to ensure that it delivers tangible benefits.
8. Internship Contracts
Internship contracts define the terms of engagement for interns, typically students or recent graduates, who work temporarily to gain practical experience in their field of study. These contracts specify the duration, scope, responsibilities, and any compensation interns will receive. Internships can be paid or unpaid, depending on the industry norms and labor laws.

Use Cases of Internship Contracts
- Talent Pipeline Development: Internships are a strategic way for companies to train and evaluate potential future employees.
- Project-Specific Work: Interns can be brought on to support specific projects where extra hands are needed without the commitment of hiring permanent staff.
- Research Roles: Academic and research institutions often offer internships to help students gain practical experience in their study fields.
- Skill Development: Companies use internships to offer practical training in skills not easily taught in classroom settings.
- Community Engagement and CSR: Internships can be part of corporate social responsibility programs, helping to build community relations and support local educational initiatives.
Internship contracts should be designed to provide meaningful learning experiences for interns while benefiting from their energy and fresh perspectives. Employers must ensure these types of employment contracts meet educational goals and comply with labor laws to provide a mutually beneficial experience.
How to Choose an Employment Contract Based on Your Hiring Needs

Choosing the right types of employment contracts is crucial for aligning your business’s strategic goals with the workforce's needs and expectations. Here’s how you can select the most appropriate employment contract based on your hiring needs:
Step 1: Identify Business Requirements
Begin by identifying the specific requirements of your business. Consider whether the job is permanent or temporary, the necessity for flexibility in terms of hours, and the nature of the job duties. Understanding these factors will guide you toward choosing between permanent, temporary, or casual employment contracts.
Here are the questions to ask yourself when identifying business requirements:
- Does the job require regular work, or can it be fulfilled temporarily with fewer hours?
- Will the new employee's employment status affect the contract terms related to minimum wage, maternity leave, or overtime?
- How should the contract address confidential information and intellectual property?
- What conditions of the employment need clear definition in a written employment contract to prevent any breach of contract?
Choosing the right types of employment contracts, whether permanent, temporary, or casual, involves carefully considering these factors. Employers must ensure that the written contract details all terms clearly to protect the business and the employee's rights.
Step 2: Evaluate Job Duration and Frequency
When assessing the job duration and frequency, consider how long and often the role requires a staff or contractor. This evaluation helps determine the types of employment contracts best suited for the position. A fixed-term or temporary contract might be ideal if the role ends on a specific date or revolves around a project. Conversely, roles requiring ongoing, long-term commitment typically necessitate a permanent contract.
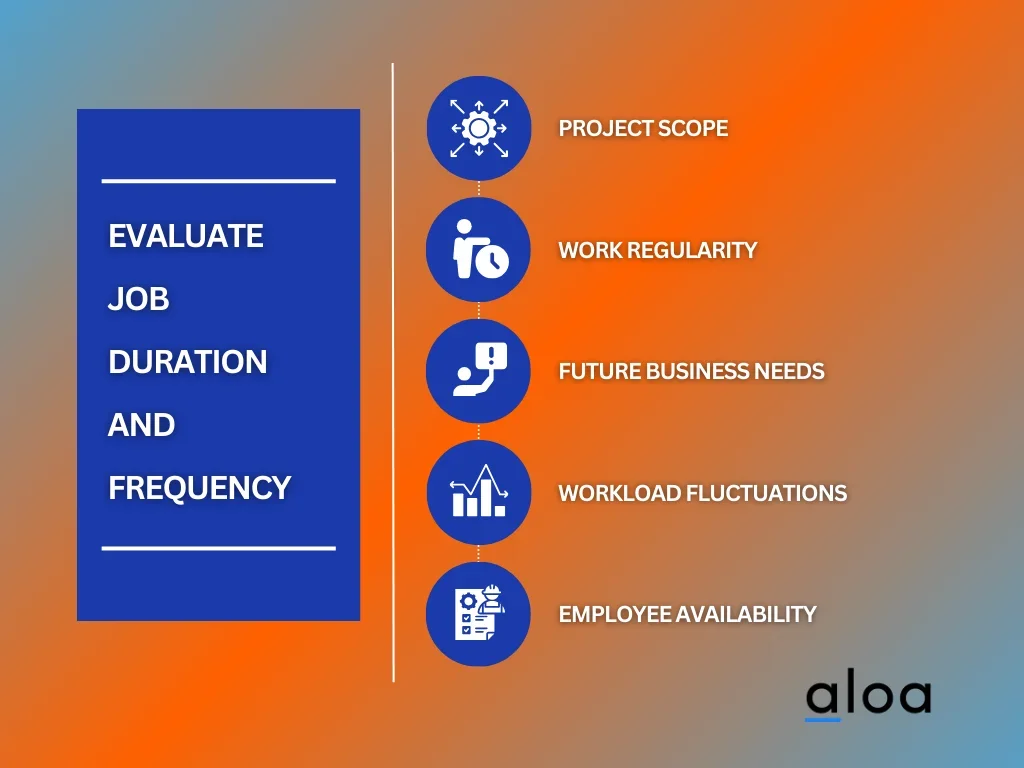
Here are five crucial considerations for evaluating job duration and frequency:
- Project Scope: Assess the scope to understand whether the job spans a short or extended period.
- Work Regularity: Determine the consistency of the work. Is the role occasional or steady?
- Future Business Needs: Consider future business requirements that might extend or alter the job's scope.
- Workload Fluctuations: Evaluate if the job will face high and low activity periods that affect duration and frequency.
- Employee Availability: Factor in the availability of suitable candidates who can commit to the proposed schedule.
Properly evaluating the job duration and frequency is vital. It ensures that employers choose the most appropriate employment contract, aligning with the project's needs and the organization's long-term objectives. This careful consideration aids in efficient staffing and optimal operational flow.
Step 3: Consider Employment Rights and Benefits
Reflect on the benefits and employment rights that are necessary for the role. Permanent contracts often come with extensive benefits like health insurance and paid leave, which attract candidates seeking job security. Temporary or casual contracts may offer fewer benefits but provide greater hiring flexibility.

Here are the things to consider regarding employment rights and benefits:
- Scope of Health Benefits: Evaluate the range of health benefits offered, including dental, vision, and general medical care, which are crucial to attracting and retaining talent.
- Pension Plans: Consider whether the employment package includes retirement benefits like pension plans, which are crucial for long-term financial security.
- Paid Time Off: Assess the provision of paid leave, including vacation days, personal leave, and sick days.
- Workplace Flexibility: Look at options for flexible working hours or remote work possibilities, which can significantly enhance job appeal.
- Employee Training and Development: Ensure there are opportunities for professional growth, which can be a decisive factor for many in choosing their employer.
Employers must strategically design employment packages that comply with legal standards and meet today's workforce's expectations. This approach helps in attracting skilled professionals and fosters a committed and satisfied workforce. Remember, a well-considered benefits package is often just as important as the salary.
Step 4: Compliance with Legal Standards
When drafting a contract, ensuring compliance with local labor laws is crucial. This involves adhering to minimum wage requirements, overtime rules, and employment rights. Such compliance not only safeguards your business against legal repercussions but also upholds fair treatment of employees. Here are some key considerations:
- Verify that the contract adheres to the minimum wage laws in your area.
- Include clear stipulations regarding overtime compensation.
- Ensure the contract respects all established employment rights.
- Regularly update the contract to reflect changes in local labor laws.
Aligning your contract with legal standards is essential. It protects your business and ensures your employees receive fair treatment. You mitigate risks and foster a positive working environment by focusing on legal compliance. This practice demonstrates your commitment to ethical business operations and respect for labor laws.
Step 5: Draft Clear Terms of Employment
Clarity is vital when creating employment terms, regardless of the contract type. Employers must explicitly define job duties, salary or hourly rates, confidentiality agreements, and termination conditions. A well-drafted contract helps ensure both parties understand their responsibilities and commitments, significantly reducing the potential for conflicts. Additionally, when engaging in business agreements, make sure to review an MSA to comprehend the specific obligations and expectations involved is important.
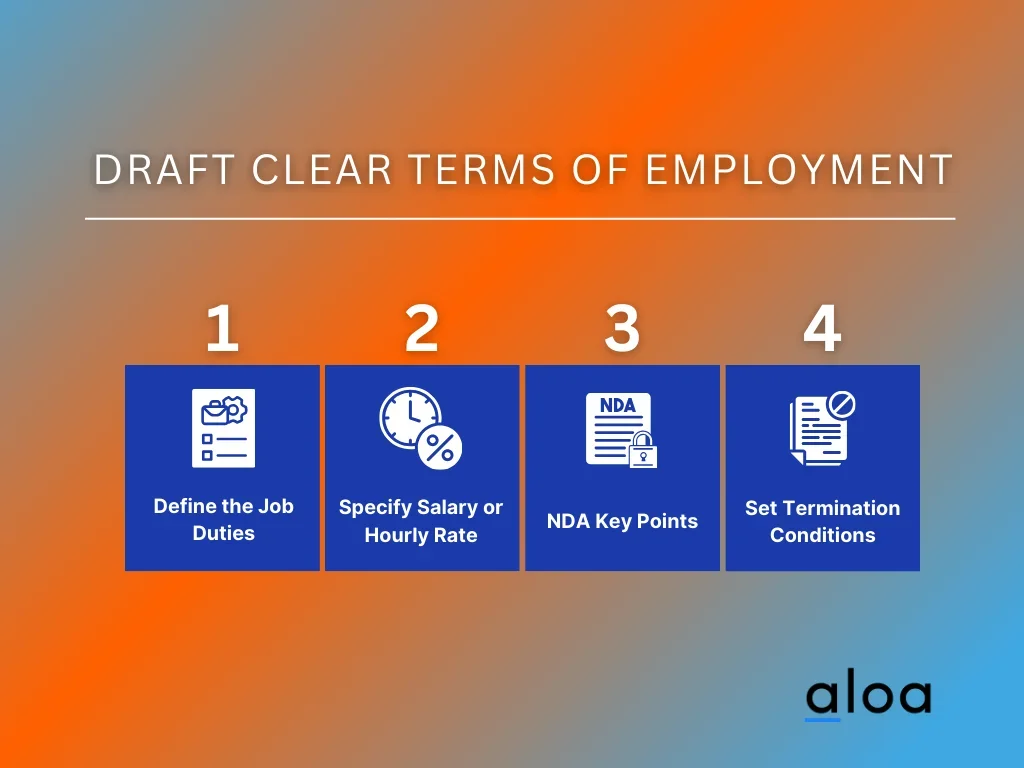
Here are the key considerations when drafting clear terms of employment:
- Define the Job Duties: Clearly outline what the employer expects from the employee. This clarity helps prevent misunderstandings and sets a clear framework for performance evaluations.
- Specify Salary or Hourly Rate: State compensation details clearly to avoid any disputes over pay. This includes any bonuses or benefits that the employee is eligible for.
- Outline Confidentiality Agreements: Protect business secrets and sensitive information with explicit confidentiality clauses. This is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and trust.
- Set Termination Conditions: Clearly articulate the conditions under which the employment relationship can end. This should include notice periods and any potential severance packages.
Drafting clear terms of employment forms the foundation of a strong employer-employee relationship. It ensures transparency and understanding, which are crucial for a harmonious work relationship. When executed with precision, this step minimizes legal risks and fosters mutual respect between the contracting parties.
Key Takeaway
Choosing the right types of employment contracts is crucial for business efficiency and legal compliance. Different contract types cater to various business needs, from full-time employment for core team members to freelance contracts for specialized tasks. Businesses can optimize their workforce management and adapt to changing demands by understanding the nuances of each contract type.
More than that, legal compliance is essential when selecting the right types of employment contracts, as overlooking regulations can lead to costly consequences. Startups, in particular, need to be vigilant about common employment law pitfalls to avoid legal disputes and financial penalties. From misclassifying workers to neglecting minimum wage requirements, understanding and adhering to employment laws is essential for long-term success.
Seeking ways to optimize your hiring strategy and ensure compliance with employment laws? Sign up for the Aloa email list to access comprehensive guides and expert insights that will help you confidently navigate the complexities of HR management. Expand your understanding and stay ahead in today's competitive business landscape with Aloa!