The rising need for advanced mapping solutions drives businesses to choose between Mapbox vs Google Maps. These platforms lead the market, offering mapping APIs and location data tailored to diverse needs. Companies rely on their robust maps APIs, geographic coordinates, and mapping data to power navigation features, address search, and mobile applications. Both deliver custom, static, and offline maps, catering to specific needs such as creating static image APIs or managing map functionality for mobile users.
Aloa is a software outsourcing agency that leverages a robust project management framework to deliver high-quality software projects. We ensure smooth integration of tools like the Mapbox GL JS and Google Maps platform. Our years of experience empower us to guide clients through complex decisions, such as selecting the best mapping platform. With access to a network of vetted development teams and modern technologies, we offer solutions tailored to your business's mapping functionality and API usage requirements.
Given our analysis, this guide compares Mapbox vs Google Maps, covering pricing models, API calls, base map options, static images API, and OpenStreetMap data. By the end, you’ll understand which platform best suits your software development goals, ensuring the best fit for your mobile app.
Let's get started!
Features and Capabilities: Mapbox vs Google Maps
Exploring the features and capabilities of Mapbox vs Google Maps reveals distinct strengths. Each platform caters to different needs, From custom and offline maps to vector data and mapping APIs. Understanding their mapping functionality helps businesses choose the right mapping provider for seamless map data integration and mobile app development.
Let’s explore the features and capabilities of Mapbox vs Google Maps.
Customization and Flexibility
Mapbox offers extensive customization options for developers needing unique maps tailored to specific use cases. The platform allows control over the map’s appearance and functionality, providing tools for various industries and creative projects. Here are the notable strengths of Mapbox’s customization:
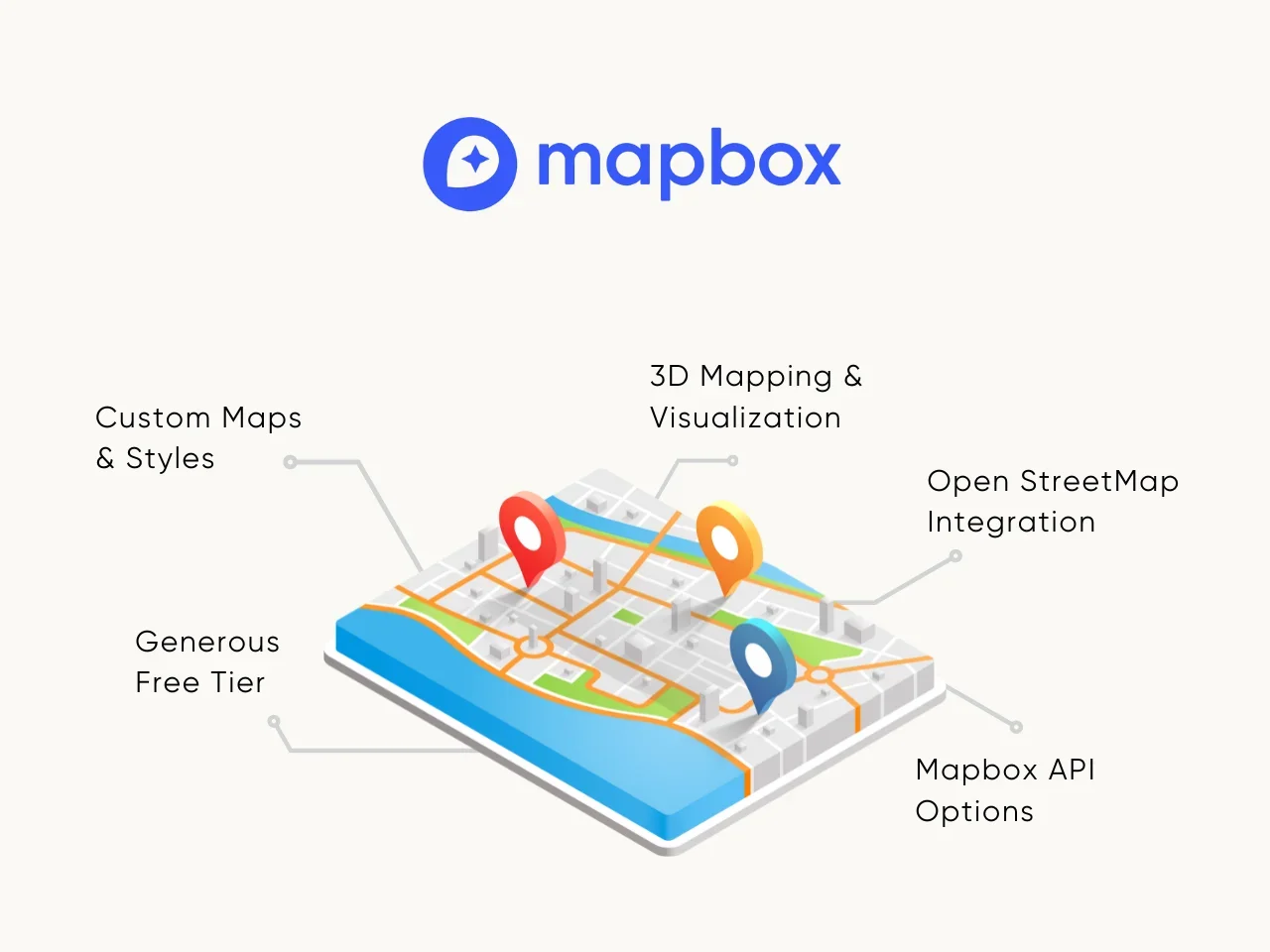
- Custom Maps and Styles: Mapbox Studio lets developers design custom maps with dynamic styling options, allowing personalized themes and layouts.
- 3D Mapping and Visualization: Advanced features like 3D rendering and satellite imagery create visually engaging experiences suitable for gaming and simulations.
- OpenStreetMap Integration: The platform relies on the OpenStreetMap project, enabling developers to update data directly and enhance accuracy for specific regions.
- Mapbox API Options: The Mapbox Directions API and other mapping APIs allow seamless routing and navigation features.
- Generous Free Tier: Mapbox offers a free plan with many free API calls, providing flexibility for testing custom solutions.
These tools make Mapbox popular for applications requiring unique visual designs or particular data flow.
Google Maps focuses on a standardized approach, providing a wide range of features with minimal effort. This makes it ideal for businesses seeking reliable, out-of-the-box solutions. Here are the highlights:
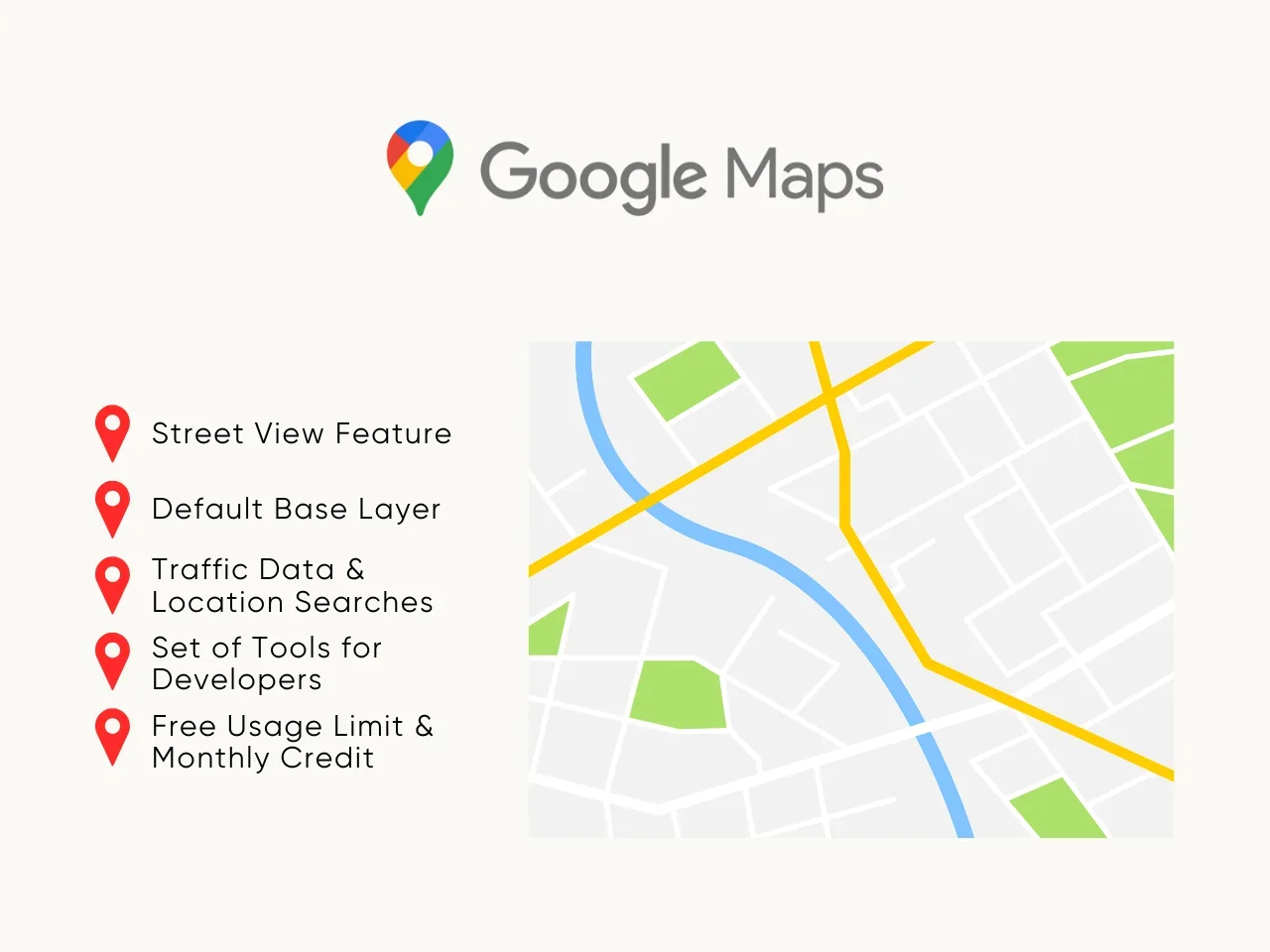
- Street View Feature: The Google Maps API includes the Street View feature, offering real-world imagery for navigation and exploration.
- Default Base Layer: Google Maps’ default base layer integrates seamlessly with various Google services, ensuring application consistency.
- Traffic Data and Location Searches: Features like real-time traffic data and advanced location searches make Google Maps a leading map provider.
- Set of Tools for Developers: The Google Maps API offers a robust set of tools with extensive documentation and examples, reducing the steep learning curve.
- Free Usage Limit and Monthly Credit: Google Maps pricing includes a free plan with a monthly credit, suitable for small-scale applications or limited map views.
These attributes make Google Maps a reliable choice for businesses prioritizing simplicity and dependability over deep customization.
Due to their customization levels, each platform excels in different applications. Mapbox serves industries needing creative custom maps, such as gaming, urban planning, and geospatial analysis. Google Maps shines in applications requiring reliable traffic data, static maps, or seamless integration with existing Google services.
Map Coverage and Data Accuracy
Mapbox provides extensive global coverage with data derived from the OpenStreetMap project, which supports frequent updates and user-contributed improvements. The platform’s focus on data granularity and customization makes it ideal for developers seeking precise and up-to-date mapping capabilities. Here are the key strengths of Mapbox in this area:
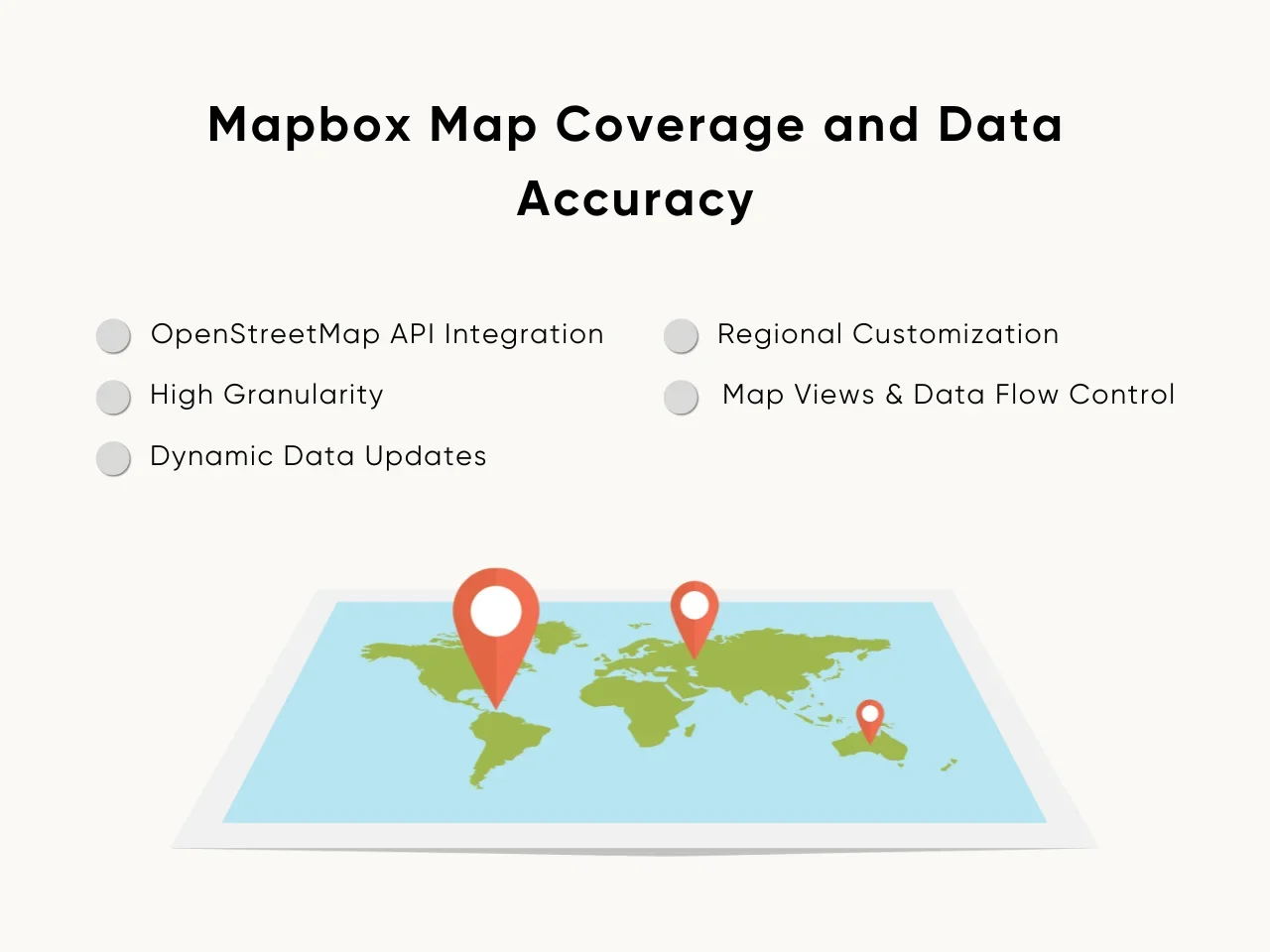
- OpenStreetMap API Integration: The reliance on OpenStreetMap ensures that maps reflect real-world changes quickly, making it suitable for applications requiring accuracy in less-mapped regions.
- High Granularity: Mapbox supports highly detailed map layers, including unique elements like building footprints and terrain data for specific applications.
- Dynamic Data Updates: Real-time updates to data ensure developers can rely on accurate information, especially for location-based services or logistics.
- Regional Customization: Developers can use Mapbox to create maps tailored to specific areas, accommodating regional needs with high precision.
- Map Views and Data Flow Control: Mapbox offers better control over map loads and data flow, helping developers optimize performance for targeted regions.
These features make Mapbox a strong choice for industries like urban planning, navigation, and location-based analytics, where accuracy and customization are critical.
Google Maps remains a trusted map provider due to its unparalleled global coverage and real-time data capabilities. Its integration with Google services ensures a seamless experience across different applications. Here are the highlights of Google Maps’ coverage and accuracy:
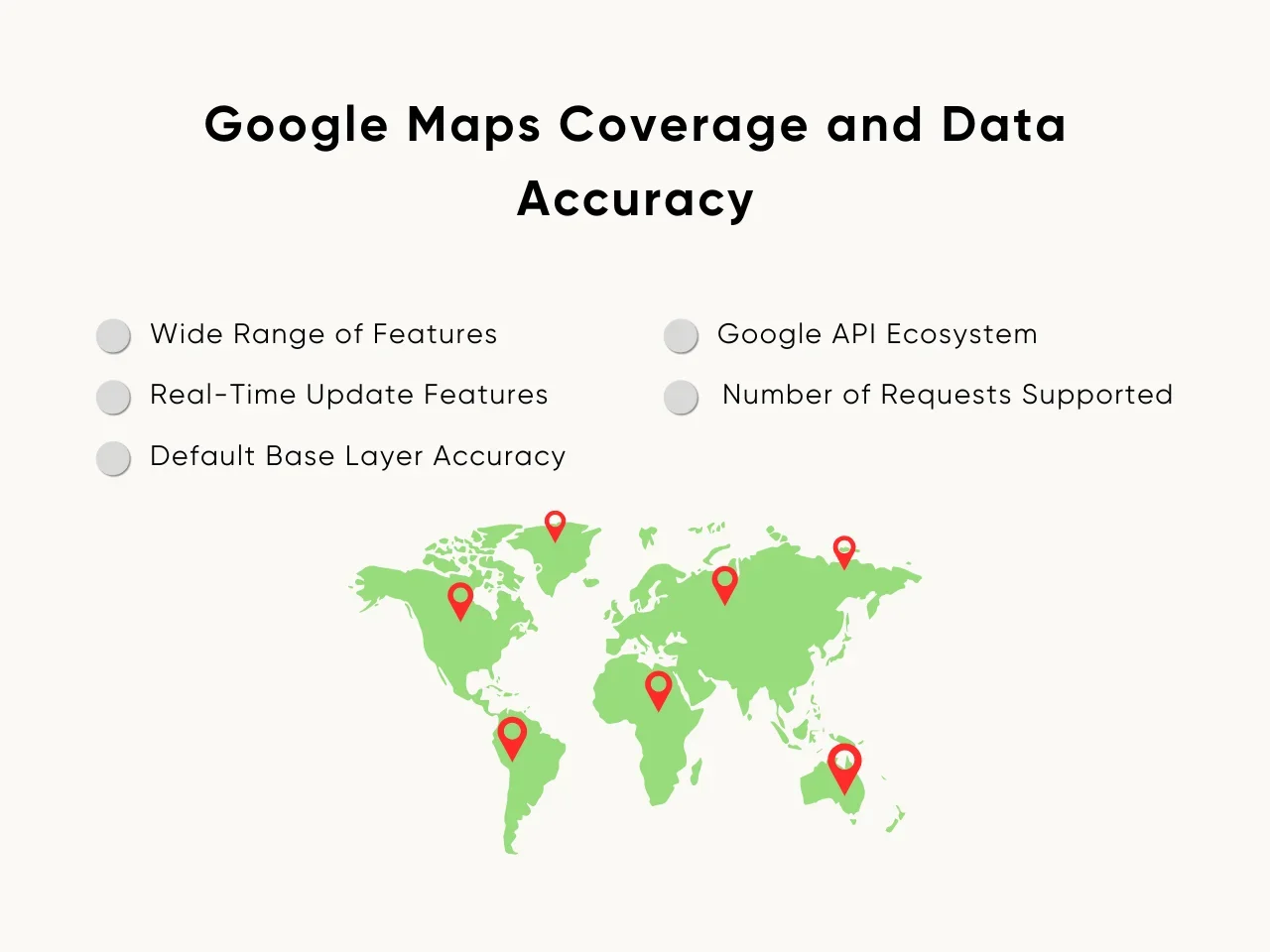
- Wide Range of Features: Google Maps offers comprehensive coverage, including satellite imagery, traffic data, and Street View, making it ideal for global applications.
- Advanced Features for Real-Time Updates: Google Maps provides up-to-the-minute traffic data and real-time changes, which are crucial for navigation and ridesharing platforms.
- Default Base Layer Accuracy: The default base layer includes highly accurate geographic and address data, catering to industries like logistics and delivery.
- Google API Ecosystem: With the Google Maps API, developers access tools that ensure reliable data accuracy and integration.
- Number of Requests Supported: The platform handles many requests efficiently, making it suitable for large-scale, high-traffic applications.
These attributes make Google Maps a popular choice for industries relying on accurate location searches, static maps, and extensive data sets.
Each platform caters to distinct needs. Mapbox excels in regions requiring frequent updates or unique customizations, such as rural areas or specialized industries. In contrast, Google Maps leads in sectors like transportation, e-commerce, and delivery, where comprehensive global coverage and real-time traffic data are essential.
Additional Features
Both Mapbox and Google Maps offer unique additional features that cater to various applications. These features enhance user experience and provide advanced tools for developers. Below is a comparison of the standout capabilities of Mapbox and Google Maps.
| Feature | Mapbox | Google Maps |
| 3D Mapping | Advanced 3D visuals for gaming and planning. | Basic 3D models in select locations. |
| Dynamic Styling | Full customization with Mapbox Studio. | Limited styling options. |
| Street View | Not available. | Real-world imagery for navigation. |
| Places API | External integrations only. | Detailed point-of-interest data. |
| Offline Maps | Supported for mobile use. | Limited functionality. |
| Traffic and Navigation | Flexible routing with Mapbox Directions API. | Real-time traffic updates and routing. |
| Satellite Imagery | High-quality, customizable overlays. | High-quality, with some restrictions. |
Mapbox appeals to developers seeking creative control through advanced customization. At the same time, Google Maps provides ready-made tools like Street View and the Places API for practical, out-of-the-box solutions. Both platforms excel in distinct areas, enabling diverse applications tailored to user needs.
Pricing Models and Cost Considerations
Understanding pricing models is essential to balance cost and functionality when choosing a mapping platform. Mapbox and Google Maps provide scalable, pay-as-you-go options with free tiers to support diverse needs. Explore their pricing structures and key considerations for managing your mapping-related expenses effectively.
Free Tiers and Pricing Plans
Mapping platforms like Mapbox and Google Maps offer flexible pricing models with free tiers to support developers and businesses of all sizes. Here are the pricing details for Mapbox and Google Maps Platform, highlighting their free tiers, pay-as-you-go models, and scalable options for developers and businesses.
Mapbox Pricing Plan
Mapbox offers a pay-as-you-go model with free tiers. Web maps include up to 50,000 free map loads monthly, charging $5 per 1,000 loads beyond that. Mobile maps support up to 25,000 monthly active users (MAUs) for free, with $4 per 1,000 MAUs after. Additional APIs, like Directions and Geocoding, offer free requests with usage-based pricing. Discounts apply as usage grows. (Mapbox Pricing)
Google Maps Pricing Plan
Google Maps Platform provides a $200 monthly credit, covering about 28,000 dynamic map loads. Beyond this, Dynamic Maps are billed at $7 per 1,000 loads for the first 100,000. APIs like Directions and Geocoding have separate pricing. Users can estimate costs and set quotas to manage expenses. (Google Maps Pricing)
Cost Efficiency for High-Volume Usage
As usage increases, Mapbox’s pricing becomes more cost-effective, offering automatic volume discounts for high traffic. For example, map loads beyond 100,000 have progressively lower rates. However, additional fees for advanced features like geocoding or routing APIs can add to costs. Businesses with complex applications may find the pay-as-you-go model advantageous but should monitor usage closely to avoid unexpected charges.
Google Maps Platform also provides tiered pricing, reducing per-unit costs at higher usage levels. The $200 monthly credit offsets initial expenses, but high traffic or complex applications—requiring extensive geocoding, routing, or Places API usage—can lead to significant costs. Features like advanced geocoding or detailed directions may incur additional fees, making Google potentially more expensive for heavy users. Tools to set quotas and track usage help manage expenses effectively.
ROI and Value for Money
When comparing Mapbox and Google Maps, understanding ROI and value for money is crucial for choosing the right platform. Each offers unique strengths based on user needs. Let's explore which platform provides better long-term value, highlighting scenarios where each excels at helping you make an informed decision for your projects.
Mapbox offers a cost-effective, customizable solution for developers seeking flexibility and scalability. Here are the scenarios where Mapbox excels:
- High Customization Needs: Mapbox offers extensive customization options, allowing developers to tailor maps to specific branding and functional requirements.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: With a more generous free tier and lower incremental costs, Mapbox is advantageous for applications anticipating high traffic or extensive map interactions.
- Offline Functionality: Mapbox provides robust support for offline maps, which benefits applications operating in areas with limited connectivity.
Google Maps provides extensive global coverage and advanced features, making it a robust choice for diverse applications. Here are the areas where Google Maps stands out:
- Comprehensive Data and Coverage: Google Maps offers extensive global coverage with detailed and accurate data, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable information across diverse regions.
- Ease of Integration: The platform provides a familiar interface and seamless integration with other Google services, facilitating quicker development and deployment.
- Advanced Features: Features like Street View and real-time traffic updates enhance user experience, particularly for navigation and location-based services.
Mapbox is suitable for projects prioritizing customization and cost-efficiency at scale, while Google Maps is preferable for those valuing comprehensive data, ease of integration, and advanced features.
Performance and Ease of Integration
Performance and ease of integration play a significant role when choosing between Mapbox and Google Maps. Both platforms offer solid capabilities, but the decision often depends on the project's specific needs, such as speed, responsiveness, and how easily they can be integrated into different programming frameworks.
Here are the key factors to consider:
Speed and Responsiveness
Google Maps boasts an impressive uptime of 99.99%, with an average API response time of approximately 100 milliseconds. This reliability ensures a smooth user experience, making it ideal for applications where speed is critical, such as real-time navigation and ride-sharing services.
Mapbox offers competitive performance, with efficient rendering capabilities that handle complex visualizations effectively. Its performance remains robust across various applications requiring dynamic data visualization.
Here are the scenarios where speed is decisive:
- Real-Time Navigation: Applications providing turn-by-turn directions benefit from Google Maps' rapid response times, ensuring timely updates.
- Ride-Sharing Services: Platforms like Uber and Lyft require swift location data processing, whereas Google Maps' speed enhances user experience.
- Dynamic Data Visualization: Mapbox's efficient rendering suits applications displaying real-time data changes, such as live traffic maps.
Ultimately, the choice between these two platforms depends on the application's specific needs. Consider whether speed or flexibility is more vital in achieving your goals. Both platforms are reliable map providers, but their unique capabilities cater to different priorities.
Developer Support and Documentation
Mapbox provides comprehensive resources for developers, including APIs, SDKs, and detailed guides for integrating mapping services into web and mobile applications. Developers can utilize Mapbox Studio for designing custom maps and leverage the Mapbox API for advanced mapping functionalities. The platform supports integration with popular programming frameworks, including JavaScript, Python, and mobile platforms, ensuring flexibility across different development environments.
Google Maps offers a suite of developer tools and extensive documentation to support integration into applications. The Google Maps API provides access to a wide range of mapping services, including Street View and Places API, facilitating the creation of interactive maps and location-based features. Google's developer resources include detailed guides and tutorials for integrating mapping services into web and mobile applications, with support for frameworks like JavaScript, Python, and various mobile platforms.
Community and Ecosystem
Mapbox has cultivated a vibrant community of developers and users who actively contribute to its growth. The platform offers extensive documentation, tutorials, and a developer forum, facilitating collaboration and knowledge sharing. Mapbox's open-source components, such as Mapbox GL JS, encourage community contributions, fostering a collaborative environment.
Google Maps benefits from Google's vast developer network, providing comprehensive resources, including detailed documentation, tutorials, and a robust support system. The platform's widespread adoption has led to a large community of developers and users who share insights and solutions, enhancing the overall ecosystem.
Key Takeaway
When comparing Mapbox vs Google Maps, evaluating each platform’s features is essential based on your specific needs and priorities. Both options offer robust solutions for mapping and navigation, but they cater to different types of users and use cases. Google Maps excels in global coverage and user-friendly features, while Mapbox provides more customization and flexibility for developers looking to build unique map experiences.
Several key considerations play a role in deciding between Mapbox and Google Maps. User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are central elements, as each platform provides distinct tools to deliver a seamless experience. Customer validation also highlights how users value each platform's ability to effectively meet navigation and data needs. Understanding these factors ensures you select the platform that aligns with your goals.
Need help choosing the right solution for your needs? At Aloa, we help you integrate Mapbox vs Google Maps seamlessly into your applications. As a full-service provider, we offer managed services to ensure your mapping solution aligns with your goals. Contact us today to learn how we can support your project.

