The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is profoundly reshaping the healthcare industry. IoMT is becoming increasingly integral to healthcare systems as technology advances, promising improved patient monitoring, data collection, and medical services. Understanding IoMT has never been more crucial in today's healthcare industry.
Aloa, an expert in software outsourcing, helps businesses and startups navigate these challenges by providing innovative solutions in the IoMT space. From smart devices and medical equipment to machine learning and IoT devices, Aloa supports healthcare providers in harnessing the power of IoMT to enhance patient care and streamline operations.
In this comprehensive blog, we delve into the world of IoMT. We explore how communication technologies, wearable devices, and medical sensors are transforming patient monitoring and remote patient monitoring. With a focus on data privacy and security, we discuss the implications of collecting sensitive medical information through IoMT devices.
Afterward, you will thoroughly understand the Internet of Medical Things, its impact on the healthcare system, and its exciting possibilities for improving the quality of care while addressing challenges such as power consumption and security threats.
Let's dive in!
What Is the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
.webp)
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is a transformative concept in healthcare. IoMT comprises medical devices and systems interconnected through computer networks and internet connectivity. It involves collecting and exchanging medical data, such as patient information and vital signs like blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, body temperature, and more.
IoMT plays a crucial role in healthcare by providing real-time monitoring, reducing human intervention, and improving the early diagnosis of chronic diseases. It ensures the security of sensitive patient information through robust data encryption and compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
The collected data from IoMT devices is analyzed using artificial intelligence and data analytics, enhancing healthcare organizations' decision-making processes. Moreover, IoMT reduces energy consumption in smart homes and remote areas. With its potential to revolutionize healthcare, IoMT is a promising technology with a bright future in the healthcare industry.
Types of IoMT devices
The Internet of Medical Things is a transformative force in the healthcare industry, revolutionizing patient care and data management. Let's explore various IoMT devices that enhance healthcare systems and patient outcomes.
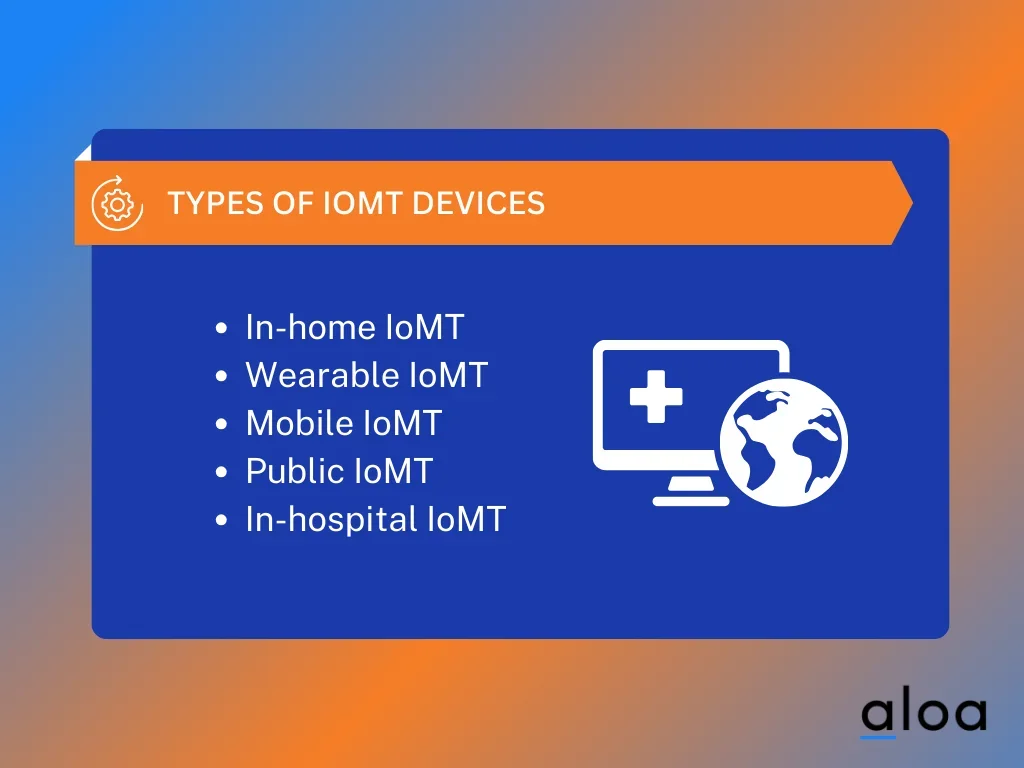
In-home IoMT
In-home IoMT devices are designed to monitor and collect patient data within the comfort of their residences. These devices include smart sensors, wearable technology, and other connected gadgets. They serve as the frontline of the IoMT system, capturing vital health information and transmitting it securely to healthcare practitioners and data repositories. In-home IoMT empowers patients to actively participate in their medical care actively, promoting early detection and proactive intervention.
Wearable IoMT
Wearable IoMT devices have gained immense popularity, offering continuous monitoring and real-time data collection. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical wearables have sensors that track vital signs and physical activity and even detect anomalies in real time. These wearables seamlessly integrate with mobile apps, allowing patients to access their smartphone health information. Wearable IoMT not only promotes healthy lifestyles but also assists in the management of chronic conditions.
Mobile IoMT
Mobile IoMT leverages the ubiquity of mobile devices to facilitate healthcare data exchange. Patients can use mobile apps to input health data, track medication adherence, and communicate with healthcare practitioners. Furthermore, mobile IoMT enables secure access to electronic health records (EHRs) and simplifies drug administration. Mobile devices with radio frequency identification (RFID) technology enhance patient safety by ensuring accurate medication administration and tracking.
Public IoMT
Public IoMT focuses on creating interconnected healthcare systems within communities. These systems integrate data from various sources, such as hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and public health agencies. By harnessing big data analytics, public IoMT identifies health trends and provides valuable insights for healthcare practitioners and policymakers. This collective approach to healthcare data management promotes community wellness and proactive healthcare measures.
In-hospital IoMT
In-hospital IoMT devices are tailored for healthcare facilities, ensuring seamless data flow and patient care. These devices include IoMT sensors, smart infusion pumps, and automated monitoring systems. They are critical in optimizing patient care, reducing medical errors, and enhancing the efficiency of healthcare practitioners. In-hospital IoMT devices are integrated with the electronic health record (EHR) system, enabling instant access to patient information and improving drug administration accuracy.
6 Steps to Implement the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The Internet of Medical Things has emerged as a transformative force in the healthcare industry, revolutionizing how healthcare providers deliver services and patients access care. Let's delve into the essential steps healthcare organizations and professionals can take to leverage IoMT effectively.
.webp)
Step 1: Establish a Solid Foundation
The first crucial step is establishing a solid foundation to leverage the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). This entails creating a robust IT infrastructure that can support the seamless integration of IoMT devices and technologies into the healthcare ecosystem.
One key aspect is ensuring network security and strict compliance with healthcare regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This safeguards sensitive patient data and mitigates potential legal and financial risks.
Investing in robust connectivity is another pivotal element. High-speed, reliable networks are essential to facilitate real-time data exchange between various IoMT devices and systems. This ensures healthcare professionals access accurate and up-to-date patient information, leading to better decision-making and patient outcomes.
Step 2: Identify Key Use Cases
In leveraging the Internet of Medical Things, identifying key use cases is pivotal. IoMT finds extensive application in healthcare, transforming how healthcare services are delivered and experienced. Some prominent use cases include:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: IoMT allows healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs and health parameters remotely, enabling early intervention and reducing hospital admissions.
- Telemedicine: IoMT facilitates virtual consultations and telehealth services, expanding access to healthcare, especially in remote areas.
- Predictive Analytics: IoMT can predict health trends through data analysis, helping healthcare providers proactively address potential issues.
- Wearable Devices and Sensors: Smartwatches and fitness trackers collect real-time data for continuous health tracking.
- Early Disease Detection: IoMT aids in the early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By analyzing patient data, IoMT enables the creation of tailored treatment plans, optimizing healthcare delivery.
Identifying and understanding these key use cases is the foundation for an effective IoMT strategy. By recognizing the potential of IoMT in these areas, healthcare organizations can tailor their implementation efforts to maximize the benefits for both patients and providers.
Step 3: Select Appropriate IoMT Devices and Technologies
When selecting Internet of Medical Things devices, it is crucial to consider several factors. First, compatibility with existing healthcare infrastructure ensures a seamless integration process. Accuracy in data collection is paramount, as the information gathered directly impacts patient care decisions.
Interoperability is another crucial consideration, as IoMT devices must communicate effectively with one another and with healthcare information systems. A harmonious ecosystem of interconnected devices enhances the overall efficiency of IoMT implementation. Additionally, continuous updates and maintenance are essential to keep devices functioning optimally, providing reliable data for healthcare professionals to rely on.
By carefully weighing these factors, healthcare organizations can make informed choices when selecting IoMT devices and technologies, benefiting providers and patients.
Step 4: Ensure Data Security and Privacy
As the Internet of Medical Things involves exchanging sensitive patient information, safeguarding this data is essential to maintain trust and compliance with healthcare regulations. Consider the following factors:

- Encryption: Encrypting data during transmission and storage is crucial to prevent unauthorized access. Advanced encryption algorithms ensure that patient data remains confidential, even if intercepted.
- Authentication: Implementing robust user authentication methods, such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication, ensures that only authorized personnel can access IoMT systems and patient data.
- Access Control: Robust access control mechanisms restrict data access based on roles and permissions, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is non-negotiable. Healthcare organizations must adhere to these frameworks, which outline strict guidelines for data protection, confidentiality, and patient rights.
Emphasizing robust cybersecurity protocols is essential. Regular vulnerability assessments, intrusion detection systems, and employee training can fortify IoMT systems against evolving threats. By prioritizing data security and privacy, healthcare providers can confidently harness the potential of IoMT while safeguarding patient information.
Step 5: Implement IoMT Solutions
Implementing IoMT solutions within the healthcare ecosystem involves a well-orchestrated approach to ensure seamless integration and optimal utilization. Healthcare professionals and IT teams play pivotal roles in this phase. Healthcare professionals provide insights into their respective departments' specific needs and workflows, helping to align IoMT solutions with existing practices.
Simultaneously, IT teams oversee the technical aspects of integration, ensuring compatibility, security, and data flow. Comprehensive training and education programs are essential to equip staff with the necessary skills to utilize IoMT effectively. These programs address device operation, data management, and cybersecurity protocols.
A carefully planned timeline guides the gradual rollout of IoMT solutions, allowing for testing, feedback, and refinement. This phased approach minimizes disruption while maximizing the benefits of IoMT in enhancing patient care and healthcare operations.
Step 6: Monitor, Evaluate, and Adapt
In the final step of implementing the Internet of Medical Things, it is crucial to emphasize the significance of ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Continuous scrutiny of IoMT systems ensures their effectiveness and helps identify potential issues or improvement areas. Data analytics plays a pivotal role in this phase, enabling healthcare providers to assess the performance of IoMT devices and systems, analyze data trends, and make informed decisions.
Additionally, fostering feedback loops within the organization is essential. Healthcare professionals and IT teams should collaborate closely to gather insights from users and stakeholders, allowing for iterative enhancements to IoMT functionality. Moreover, it is imperative to recognize the ever-evolving nature of healthcare needs and technological advancements. Agility is key in adapting IoMT solutions to meet changing requirements and harnessing emerging technologies to stay at the forefront of healthcare innovation.
Common Challenges with Implementing IoMT
Implementing the Internet of Medical Things in the healthcare industry has its fair share of challenges. Let's explore healthcare organizations' five common challenges when integrating IoMT and provide possible solutions.

Interoperability Issues
One of the primary challenges in IoMT implementation is the interoperability of various medical devices and systems. Different manufacturers use diverse communication protocols, making it difficult for devices to exchange data seamlessly.
Solution: Standardization is critical. Healthcare organizations should prioritize the adoption of standardized communication protocols and ensure that all IoMT devices comply with these standards. This will enable smoother data exchange and compatibility across different devices.
Data Security Concerns
With the sensitive nature of medical data, security is a paramount concern. Healthcare organizations must safeguard patient information against cyber threats and breaches.
Solution: Employ robust encryption methods, access controls, and regular security audits. Training staff on cybersecurity best practices is also essential to create a culture of security awareness within the organization.
Privacy Compliance
Compliance with data protection regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is mandatory in healthcare. Ensuring IoMT solutions adhere to these regulations can be challenging.
Solution: Develop a comprehensive compliance strategy that includes regular audits, risk assessments, and continuous Internet of Medical Things systems monitoring. Engage legal experts to ensure full compliance with privacy regulations.
Resource Constraints
Many healthcare organizations face budgetary limitations and resource constraints when implementing IoMT. Purchasing and maintaining IoMT devices can be costly.
Solution: Explore cost-effective IoMT options, such as leasing equipment or partnering with technology providers that offer scalable solutions. Budget planning and seeking government grants or incentives can also alleviate financial burdens.
Resistance to Change
Resistance from healthcare professionals to embrace IoMT technology can hinder its successful implementation. Staff may be accustomed to traditional methods and prefer adopting new digital processes.
Solution: Provide comprehensive training and education programs to familiarize healthcare staff with IoMT benefits and functionality. Involve them in decision-making and demonstrate how IoMT can improve patient care and workflow efficiency.
Potential Impact of IoMT on Healthcare Industry
The Internet of Medical Things is poised to profoundly impact the healthcare industry, revolutionizing how healthcare is delivered and managed in 2024. This transformative technology is gaining momentum, and its potential benefits are becoming increasingly evident.
Let's explore five key ways IoMT is set to reshape the healthcare landscape:
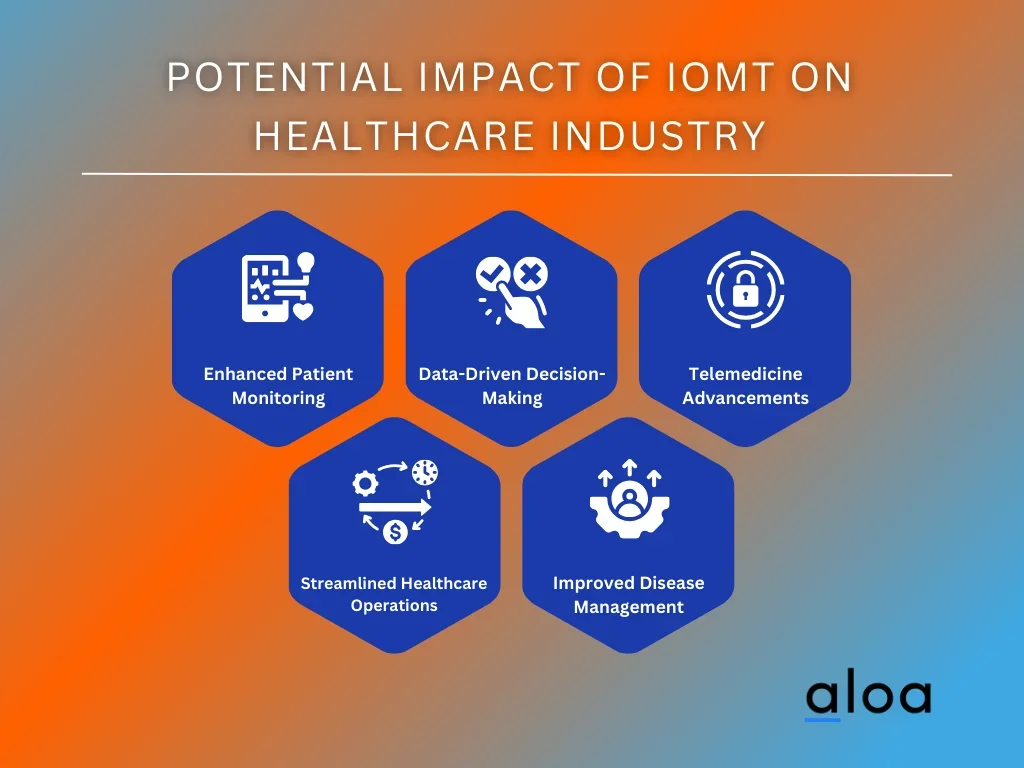
Enhanced Patient Monitoring
IoMT enables continuous and real-time monitoring of patients, both within healthcare facilities and remotely. Wearable devices and sensors can collect vital signs and health data, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patient's conditions more closely. This real-time data can lead to early intervention, reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
The massive influx of data IoMT devices generates provides a wealth of information for healthcare professionals. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can process this data to identify trends, predict disease outbreaks, and optimize treatment plans. This data-driven approach enhances clinical decision-making, resulting in more personalized and effective patient care.
Telemedicine Advancements
IoMT plays a pivotal role in advancing telemedicine. Through IoMT-connected devices, patients can have virtual consultations with healthcare providers, facilitating access to medical expertise regardless of geographical barriers. This expansion of telemedicine improves healthcare accessibility, particularly for individuals in remote or underserved areas.
Streamlined Healthcare Operations
Internet of Medical Things streamlines administrative tasks and healthcare operations. Automated inventory management, equipment maintenance, and patient scheduling reduce operational costs and free healthcare staff to focus on patient care. Additionally, IoMT enhances the tracking and tracing of medical assets, improving overall efficiency.
Improved Chronic Disease Management
Chronic disease management benefits significantly from IoMT. Patients with diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease can use connected devices to monitor their health at home. Healthcare providers can remotely access this data to adjust treatment plans and provide timely interventions. This approach promotes proactive healthcare management and reduces the burden on hospitals.
Key Takeaway
The Internet of Medical Things is a pivotal innovation within the healthcare industry, poised to revolutionize how we approach patient care and healthcare management in 2024. With its seamless integration of medical devices, data systems, and advanced communication technologies, IoMT holds the potential to usher in an era of enhanced patient monitoring, data-driven insights, and cost-effective healthcare delivery.
Healthcare professionals and organizations must proactively explore IoMT solutions to stay at the forefront of this transformative wave. By embracing IoMT, they can streamline healthcare processes and improve patient outcomes through early disease detection and personalized treatment plans. Healthcare practitioners must adapt to this evolving landscape, harnessing the power of IoMT to provide better patient care.
As we move forward, the research and implementation of IoMT in the healthcare sector will be critical. Continual innovation, data security measures, and interoperability standards will be essential components of this journey. Healthcare professionals must stay informed and collaborate with technology providers to ensure the successful integration of IoMT solutions into their practices.
For more information and resources on the Internet of Medical Things and its applications in healthcare, please do not hesitate to contact us at resources@aloa.co.