User experience design and user interface design are two distinct disciplines, even though interchanged at times, eventually resulting in hiring the wrong designer for a project. This makes understanding the key differences between user interface vs user experience design during the employment process even more crucial.
There are many ways to tell them apart by their roles and responsibilities. In general, user interface refers to the visual elements of a product you interact with, like the colors, buttons, icons, screens, and pages, while user experience refers to how you feel while using that product.
In this article, we’ll be discussing user interface vs user experience; their meaning, difference, and the roles of user interface designers and user experience designers. By the end of this article, you’ll know the key aspects that distinguish them from one another, and how they function together.
Let’s dive in.
What Is User Interface?

User interface refers to the elements and layouts we engage with on websites, apps, and other product types daily. These include buttons, widgets, texts, icons, images, slides, and other visual design elements we encounter when using a product.
In simpler terms, the user interface deals with every element you can engage with while using a digital product. Collaborating with professional UI UX design services ensures meeting all business needs by enhancing the touchpoints people have with your product.
What Is User Experience?
User experience refers to our journey while using a product. How we feel while interacting with the elements, how easy it was to use and understand, or how difficult it was. This journey starts from where we learn about a digital product, all the way to when we acquire and make use of it. Simply, all the touchpoints people have with your product.
In simple terms, the overall user experience is based on the complexity of a product or service, what was the customer experience like upon getting there, and whether it serves the purpose. This process is also known as user flow, which refers to our journey through a product.
1. What Is The Difference Between User Interface And User Experience?
Since UI/UX design works together, their functions can easily be confused. Let us take a deeper look into some of the key features of user interface and user experience that differentiate them from each other.
1.1 Key Features Of User Experience
- UX is concerned with how we feel about a product after using it.
- UX is concerned with a user’s experience in the journey when using a product.
- User experience is about our interaction with a brand, its services, and its product.
- UX is not limited to only digital products and their functions, they also involve offline aspects like marketing the product.
- A user experience designer is more concerned about the problems we face while using a product. Problems like how easy it is to navigate to a page, how fast the pages load, or how convenient the icons are to interact with, are all user experience based.
1.2 Key Features Of User Interface
- It is specific to the platforms we use to interact with products.
- The user interface is limited to products only without a company’s services.
- UI is focused on the physical appearance, attributes, and functions of the product.
- In the case of apps, the user interface journey begins after end-users have acquired and activated it.
- UI is a link between us and the problems we need solutions for. Problems end-users are facing remains unsolved until the user interface stage is reached. This means until an app or site is activated or accessed, users will not find what they need.
2. User Interface Design Vs User Experience Design: What Is The Difference?

User experience on its own can function in both digital-based products and offline products and services, but user experience design can only be applied to digital-based products.
Here are a few differences between UI design and UX design:
- User experience design focuses on the creation of products that are easy to use, easy to navigate, and solves the problems we seek them out for. On the other hand, user interface design refers to the visual elements, design systems implemented, the functions of each element, the layout of the pages, graphics design, and typography.
- The UX design process involves carrying out user research to get insights into how target users feel about a product in the process of creation before it gets to the final stage while the UI design process is a result of the data gathered from this research.
- User experience design involves creating low-fidelity wireframes and prototypes for the end-users to test, which are the foundation of these products. Similarly, UI design also involves the production of high-quality mockups of a product, graphics design, and layouts.
- A good UX design involves carrying out user research, usability testing, and the theoretical aspects of the design system.
3. What Does A UI & UX Designer Do?
Let's now examine the work scope that sets UI and UX designers apart from one another.
3.1 UX Designer Work Scope
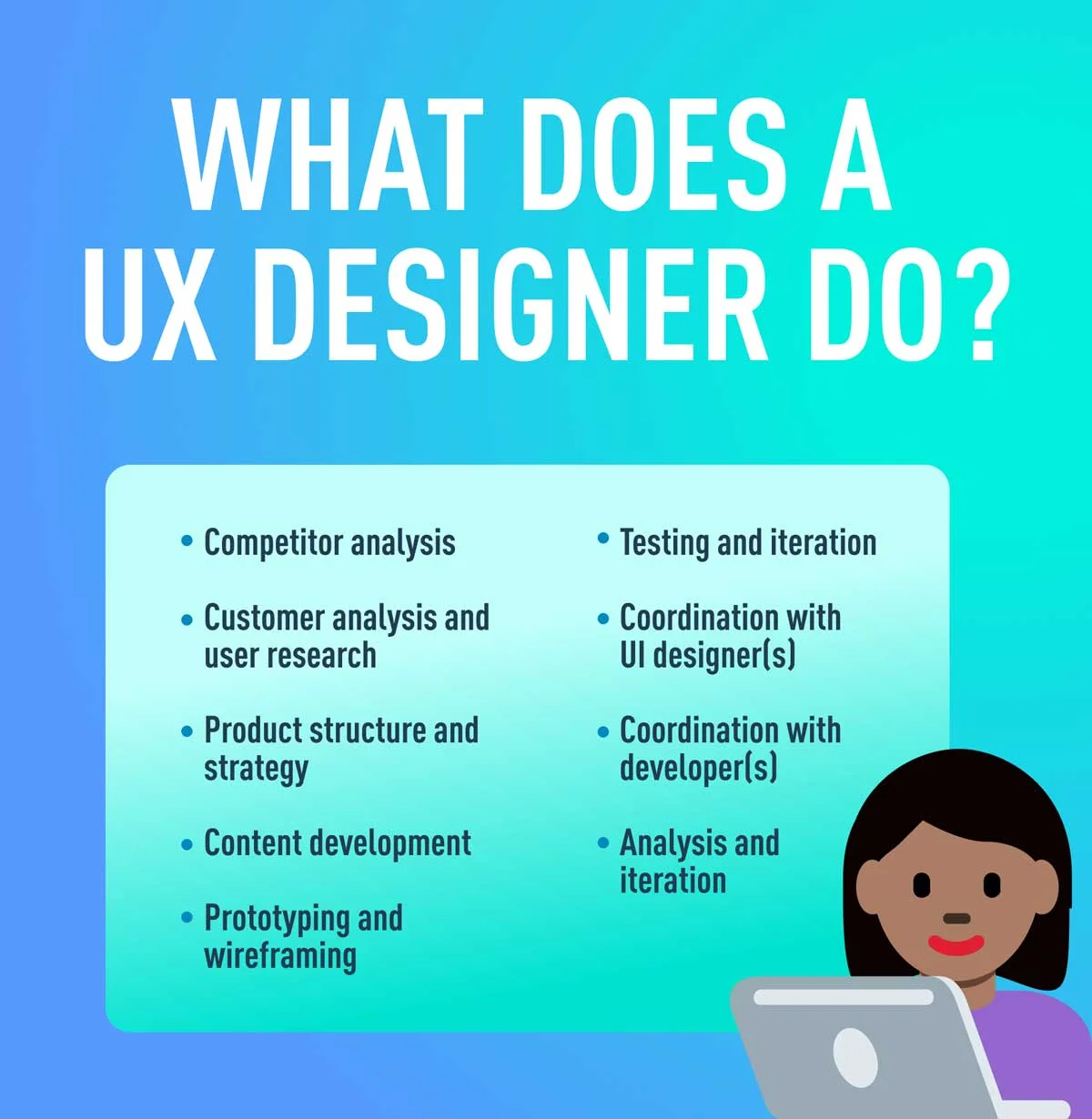
UX designers focus on how users interact with products. Functionality, accessibility, and satisfaction are the goals of a UX designer for creating products. Although UX is often associated with digital products, UX design can also be applied to aspects like customer service, interactions with brands, and many other real-life applications. There are several common tasks for a UX designer, some of which are:
- Creating user personas based on target customers’ needs
- Identifying problems and validating product design choices through user testing
- Carrying out usability studies and trying out new products with real participants
- Prototyping and creating wireframes to discover what a final product will look like
- Making use of user journey maps to analyze how customers interact with a product
- Working with UI designers, developers, and stakeholders in creating the best final product possible
- Tools, locations, and methods used to carry out user research activities are arranged by user experience designers
- Identifying the goals, needs, behaviors, and pain points linked with the interaction with the product through user research
- Development of strategy, planning, execution, and analysis of projects after they are implemented is also the job of a UX designer
- They create low-fidelity prototypes, develop user research questions, set up the locations, and get participants to try out products
- UX designers also work on content strategy, which includes the planning, creation, and carrying out of content like texts, images, and other elements needed for a product
- They ensure they stay up to date with changing trends in delivering services to the end-users, keeping track of product performance, and improving existing designs
3.2 UI Designer Work Scope
UI designers create the graphical portions of mobile apps, websites, games, and devices that users interact with directly. Digital products are exclusively UI-based. It is the job of UI designers to ensure that apps and websites are both visually appealing and easy to navigate. UI designers are responsible for a variety of tasks including:
- Showing how the final design for a product will look like
- Converting designs into finished and working products with the help of developers
- Picking the colors and fonts for products, except for branding elements that already have a working design system
- Oftentimes, UI designers might need to start a brand’s identity from scratch, while some brands already have a design system available
- Creating interactive elements like animations, and inserting images and videos where appropriate, are all the responsibilities of a user interface designer
- Making functional interactive elements like scrollers, buttons, icons, toggles, menus, drop-down menus, text fields, animated buttons and shapes, and many more
- UI designers are tasked with maintaining a brand’s style across the board. The brand’s icons, colors, fonts, and others remain the same across all platforms and devices
- Organizing layouts for responsive designs and creating vectors that can be easily resized on different kinds of devices end-users might use to access the product
In essence, UI/UX designers handle both UI design and UX design responsibilities. They are fully involved in the theoretical and practical aspects of the design process. UI and UX design responsibilities in the app and web design complement each other and this is why sometimes, smaller brands prefer to hire one person for both roles rather than separate individuals.
Nobody understands these fundamentals better than Aloa. We only provide you with the best and most experienced UI and UX designers for your outsourced project after carefully evaluating your preferences and professional requirements. We also have a state-of-the-art project management platform, so you’ll receive updates on the project's progress in a more transparent manner.
4. Essential Skills For UI & UX Designers

In charge of the design and implementation of digital products and services, UX and UI designers should possess a wide range of essential skills.
UI and UX designers both require different skill sets to perform their job roles. Below are some of the major skills that user experience and user interface designers should possess:
4.1 Wireframing & Prototyping
A significant skill for UX designers is to test the structure and functionality of software and services. Wireframes serve as an outline for each component of a product interface, demonstrating how it functions rather than just how it appears. Using prototypes, designers may test a product or service's usability and ensure that it functions properly before it is put into production.
4.2 User Research
To determine what people want or anticipate from a product or service, UX designers conduct in-depth user research using various methods including focus groups, interviews, surveys, and questionnaires.
Making decisions about the products they design based on data can benefit UX designers if they have a solid understanding of how to use efficient research tools. While some firms combine UX design and research into one function, others allocate these duties to a UX researcher role.
4.3 Visual Design
A large percentage of UI/UX designers incorporate visual design into their routine tasks. A website, software, or other product forms may include elements made by UI designers using visual design techniques.
While doing so, UX designers largely rely on their design expertise to produce working prototypes. Additionally, as usability and design go hand in glove, anyone looking to start a career in UI/UX should be familiar with visual design.
4.4 Information Architecture
The process of organizing and arranging content on websites, web and mobile apps, and other software applications is known as information architecture (IA). Effective content organization, labeling, and structuring are the main goals of information architecture.
The objective is to assist users in comprehending their current location, their findings, and what to anticipate from the solution they are utilizing.
4.5 Copywriting
A significant proportion of product development and design rely on copy in a certain way. The importance of good copywriting for both UX and UI designers stems from the fact that it is a crucial element of successful user interactions.
A product's usability and visual design both benefit from strong content. The tone of voice of the copy is crucial to the design process since it contributes to the visual identity of a business.
4.6 Other Responsibilities Of A UI/UX Designer
Apart from the key responsibilities mentioned above, there are many other tasks carried out by UI/UX designers that are also essential in creating websites, apps, and other digital-based products. Let’s take a look at some of them.
User Interface:
- Animation
- Typography
- Iconography
- Color theories
- Interaction design
- Design system creation
- Creating design patterns
- High-fidelity prototype creation
User Experience:
- Creating user personas
- Crating product strategies
- Conducting usability research
- Iteration and testing of low-fidelity prototypes and wireframes
5. Similarities Between UI/UX Design

Two of the most perplexing terms in the industry are UI and UX. Although UI and UX go hand in hand and neither can exist without the other, however, becoming a UI designer does not require knowledge of UX design. Now let's examine the key similarities between UI and UX:
- While UI is built on making navigation simple for users, UX is based on the user journey. However, the striking similarity between the two is being conscious of user needs. Both the UI and UX designer are concerned with helping the end-users reach their goals while making use of the product.
- UX and UI share the same objective, which is to ensure that the users are happy with the final product.
- Design Thinking: The goal of UX and UI designers is to create user-friendly designs, conform to design principles, and make use of familiar elements.
6. Why Should You Hire a UI/UX Designer?
It is important to know what role UI/UX design plays in the development of any online product or rendering of any kind of service since the differences and in-depth analysis of what they both stand for are now clear.
Now let’s learn why they should be implemented in design systems for products and services. Below are a few benefits of UI/UX design:
- Hiring UI/UX designers for the development of your product ensures that you deliver high-quality and brilliant designs to attract and engage users.
- It helps optimize the user flow of your app or website. When users can easily navigate through your app or site, they can easily find what they need, and this helps in boosting conversion rates.
- Proper user interface design helps with guiding users of your products in what to do next on your site, by using proper page layouts, clear call-to-action, and buttons.
- A graphical user interface stems from good research by the user experience team and this helps to increase ROI, boost conversions, and help you grow a successful brand.
Conclusion
Irrespective of the differences between user interface vs user experience, they are both important in the design process of any kind of digital product. They are necessary for the success of any business, may it be a startup or a Fortune 500 company. A professional that is grounded in both will always be a valuable asset to any company.
And Aloa can help you in your quest for finding the right candidate. We employ a strict screening procedure when hiring, ensuring that you only receive top-tier experts for your projects. We frequently hold boot camps and training sessions to keep our product management at the top of the game.
So whether you want to hire separate individuals for the roles of user interface and user experience, or you'd rather have one person handle both tasks, we’ve got you covered. Visit our website or email us at [email protected] and we will be glad to assist you in finding the best resource for your design.














